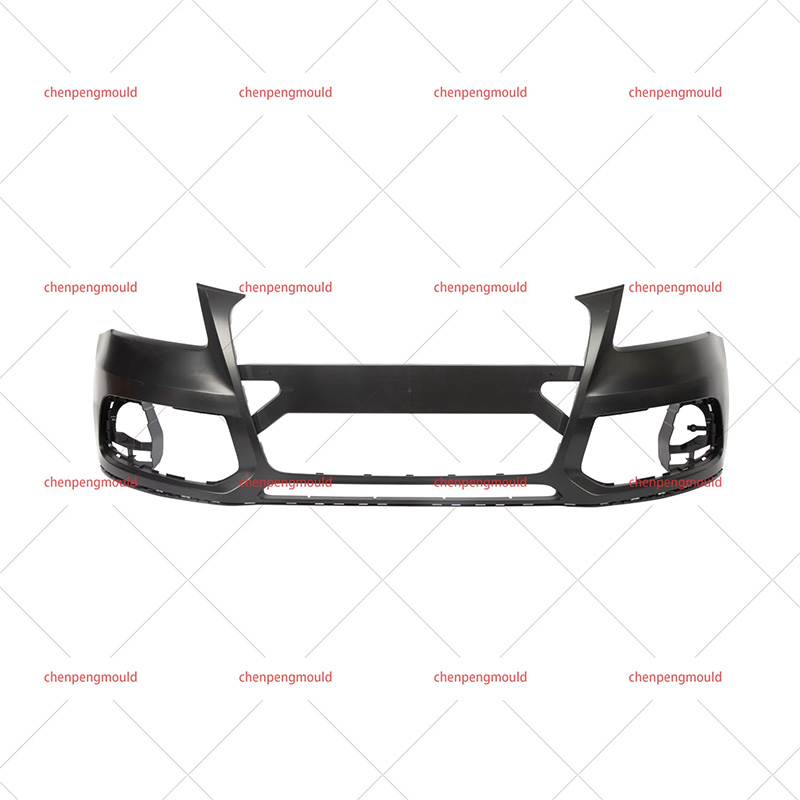
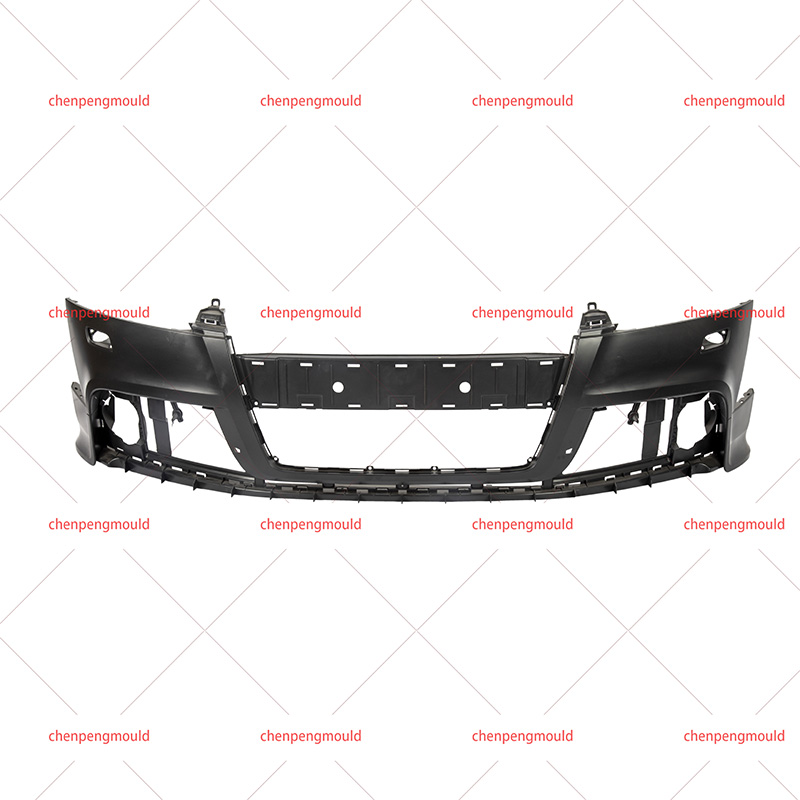
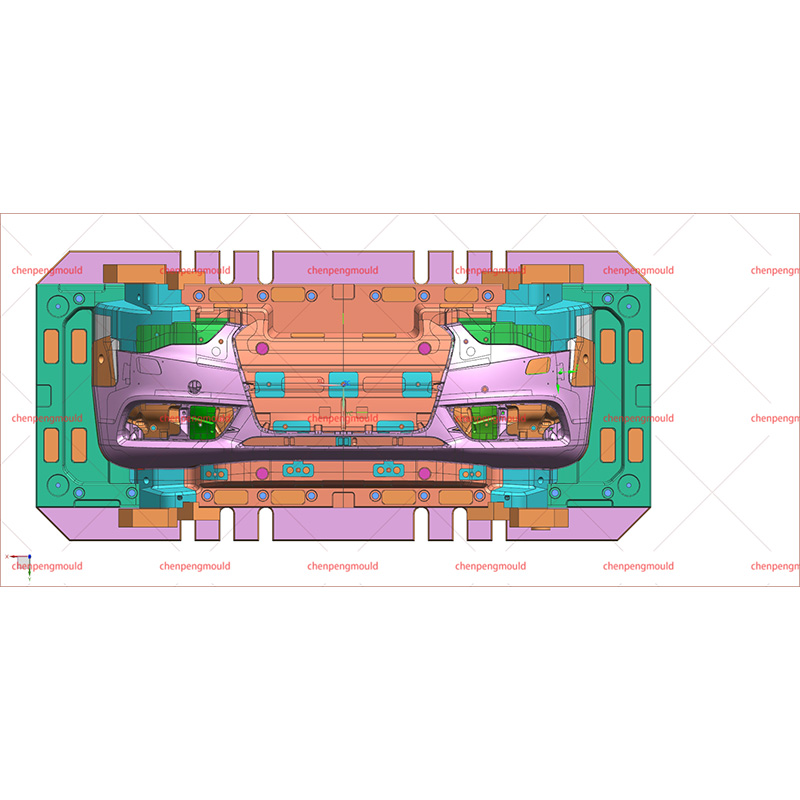
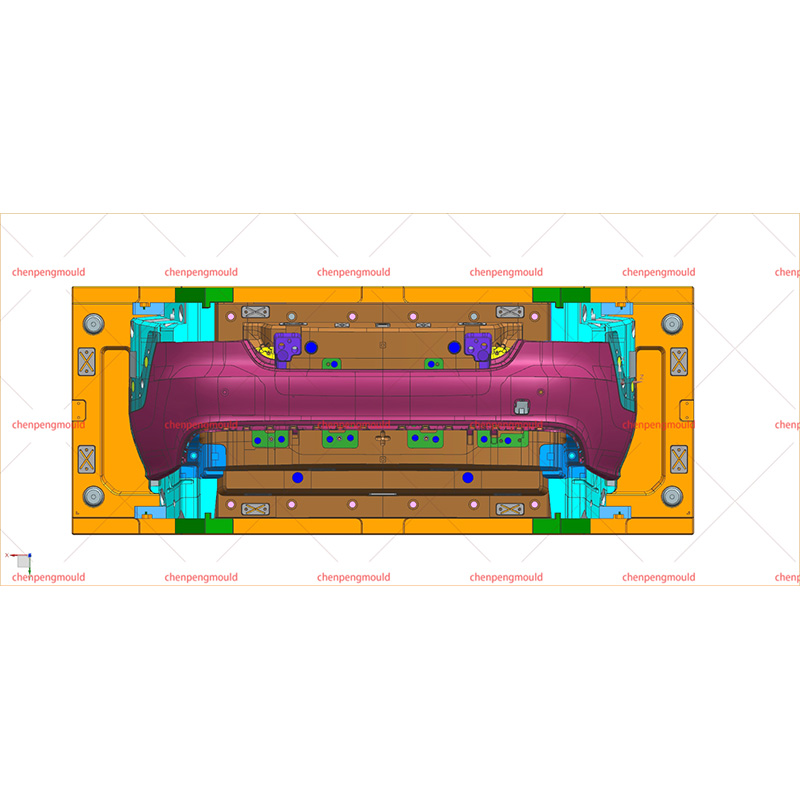
The success of rear bumper moulding largely depends on controlling variables like material quality, mould temperature, injection pressure, and cooling rates. Any miscalculation or deviation in these parameters can defective bumpers that fail to meet the required specifications.

One of the common issues caused by incorrect operation in rear bumper moulding is dimensional inaccuracies. If the injection pressure or temperature is too high or too low, the material may not fill the mould cavity properly, incomplete or uneven moulding. This results in bumpers that are either too large, too small, or improperly shaped.
Dimensional inaccuracies can have serious consequences, such as:
Poor Fitment: A bumper that does not match the vehicle's specifications may not fit properly, resulting in gaps, misalignments, or improper attachment to the vehicle frame.
Increased Rework: Mismatched bumpers will require rework or even complete remanufacturing, adding to production time and costs.
Quality Control Failures: Even minor dimensional deviations can cause a part to fail inspection, delaying the production process.
Surface quality is crucial in automotive parts, particularly rear bumpers, as they directly affect the vehicle's appearance. If the mould temperature is not carefully controlled or the cooling rate is incorrect, surface defects such as warping, uneven texture, or sink marks can appear on the finished bumper. These defects not only degrade the bumper's appearance but also impact the structural integrity of the part.
Surface defects can be caused by:
Uneven Cooling: Rapid cooling can cause warping, while slow cooling can result in shrinkage, both poor surface finish.
Material Overheating: Excessive heat can degrade the material, causing discoloration or surface bubbles that mar the bumper's visual quality.
Injection Speed Issues: Incorrect injection speed may uneven filling, leaving air pockets or irregular surface finishes.
These surface imperfections may require extensive finishing work, which further increases costs and production time.
A rear bumper needs to provide protection during low-speed collisions, so its structural integrity is a key factor. Incorrect operation in the moulding process can weak spots in the bumper, reducing its ability to absorb impact and protect the vehicle.
Key issues that can result in weakened structural integrity include:
Incorrect Material Selection: Using materials that are too soft or have not been adequately processed can cause the bumper to lack the necessary rigidity.
Insufficient Injection Pressure: Low pressure during the injection phase can air pockets or voids within the bumper, weakening the material and compromising its strength.
Inconsistent Wall Thickness: If the mould is not designed correctly or the material is not injected uniformly, areas of the bumper may have inconsistent wall thickness. Thinner sections are more prone to damage during impact.
Weak bumpers not only fail to meet safety standards but also endanger the vehicle occupants and increase the likelihood of legal liability for the manufacturer.
Incorrect operation in rear bumper moulding can cause significant delays and higher costs due to defects that require rework or remanufacturing. For instance, if the wrong material is used or a mould misalignment occurs, a whole batch of bumpers may need to be scrapped. This wasted raw materials, added labor costs, and extended production times.
Additionally, if poor-quality bumpers pass through inspection, they may cause downstream problems, such as assembly delays or increased warranty claims, further raising costs for manufacturers.
Inaccuracies in the moulding process can significant waste. If the moulding parameters are not optimized or the process is mishandled, scrap rates can increase. This includes defective parts that cannot be used in production and the excessive use of raw materials due to inefficiencies. The environmental impact of increased waste and the cost implications of disposing of defective parts can be considerable, making it imperative to get the process right the time.




 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666