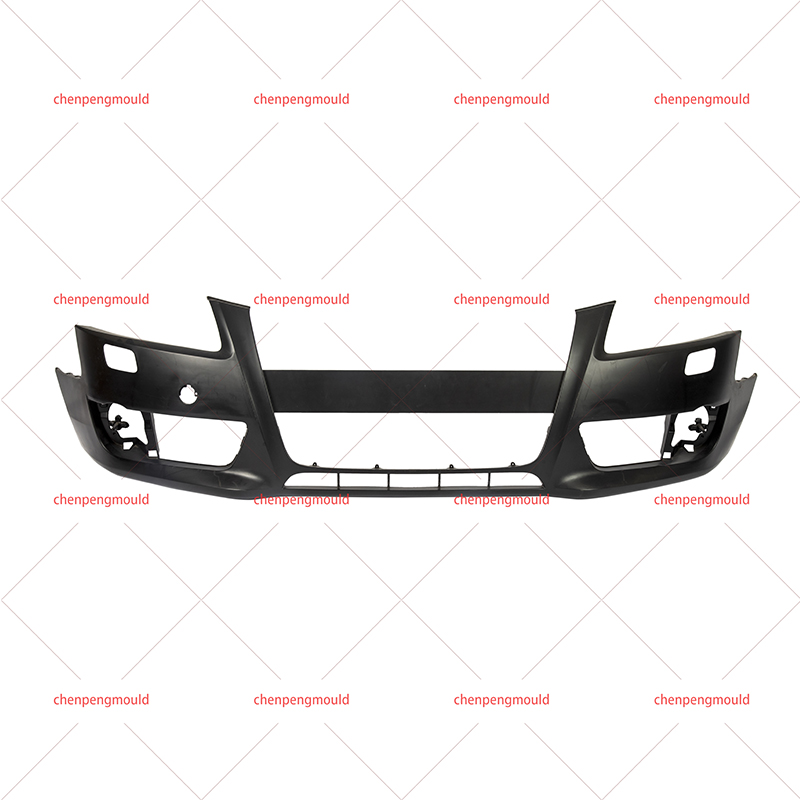
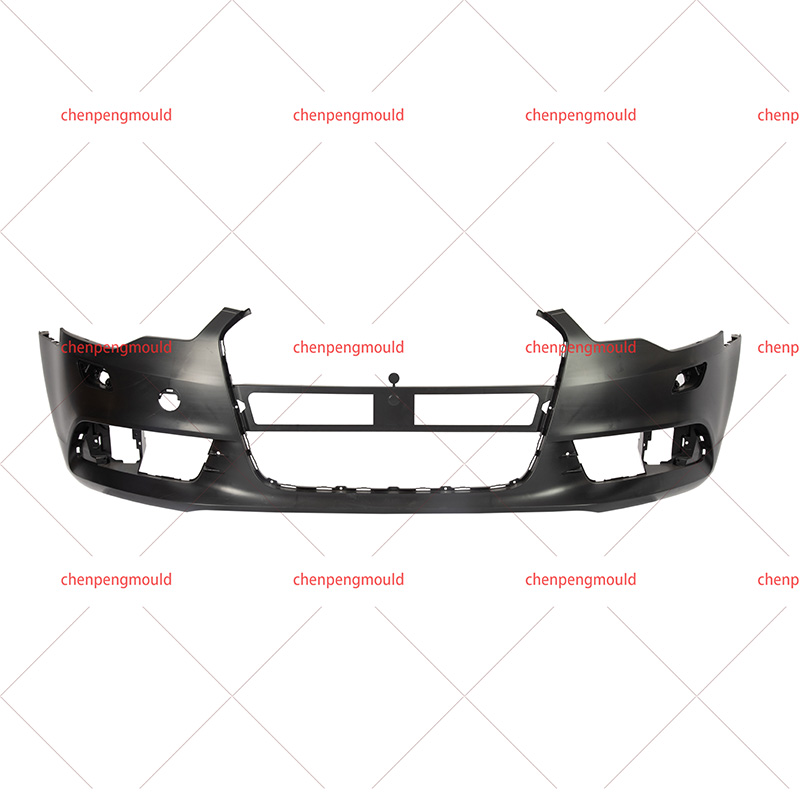
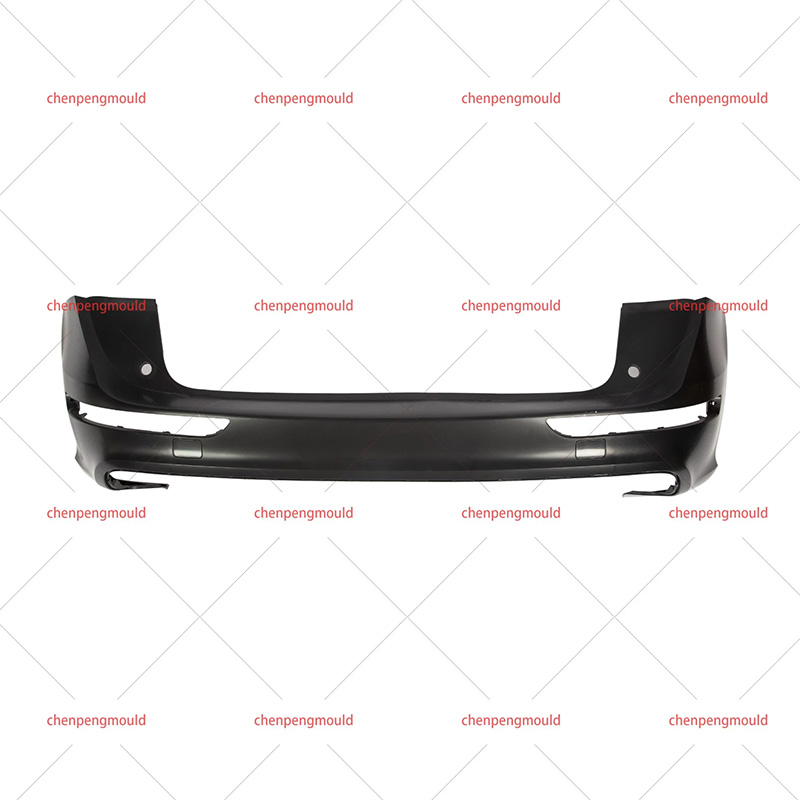
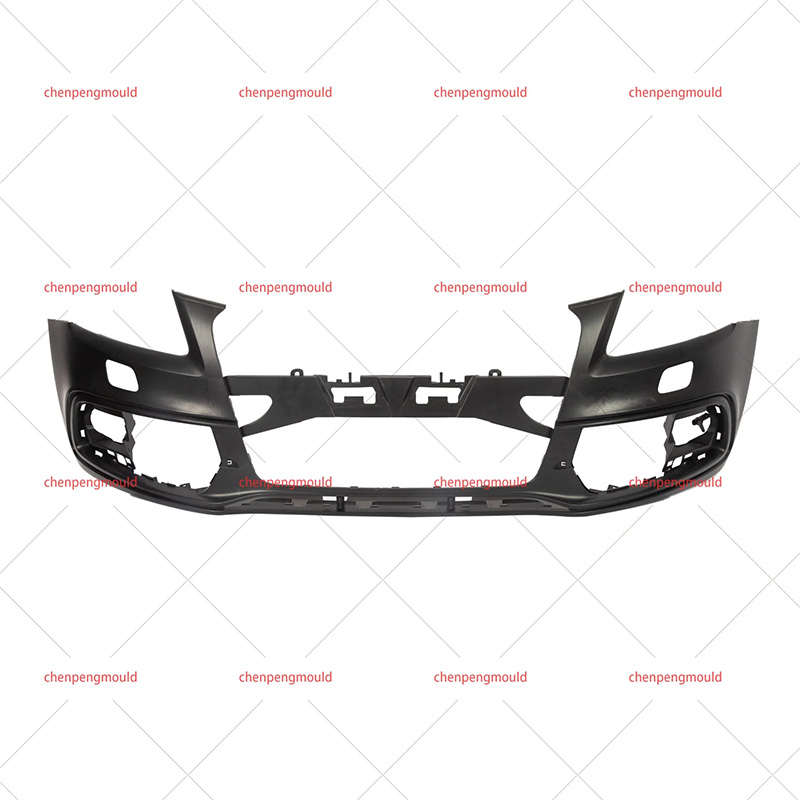
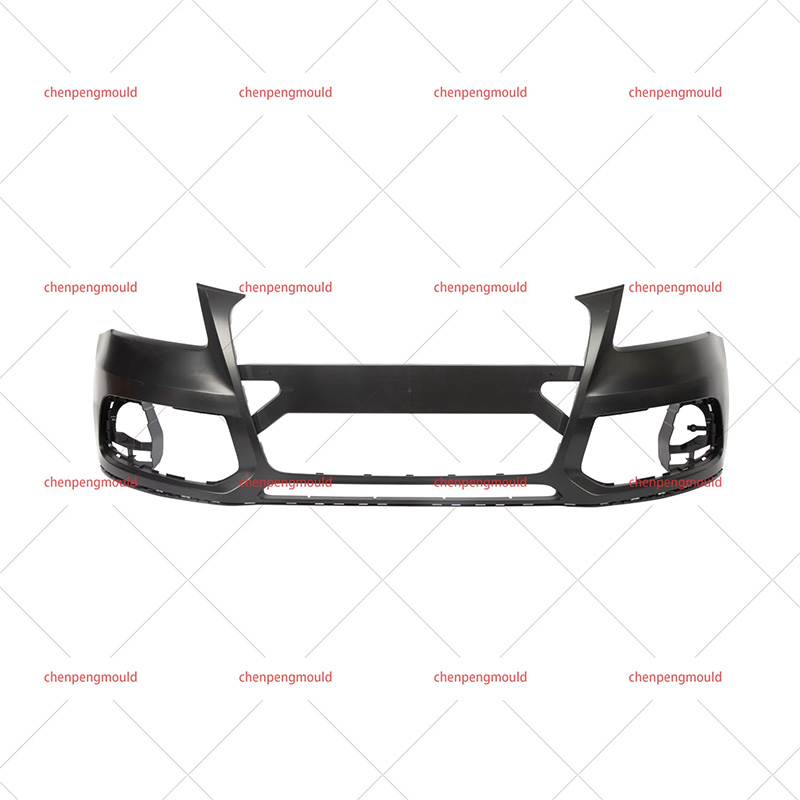
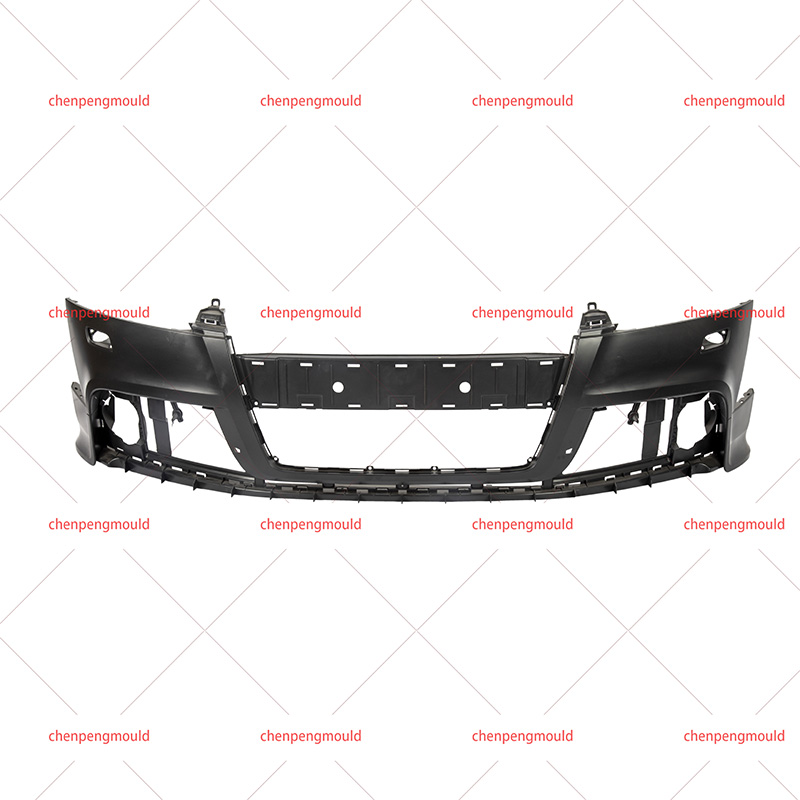
The molding process—often involving plastic injection molding—allows manufacturers to shape bumpers that contribute to both function and appearance. To fully understand its impact, this essay examines the advantages and disadvantages from production efficiency, design flexibility, safety, cost, and sustainability perspectives. With real-world examples and logical reasoning, we can evaluate its practical value in today’s automotive industry.

How does molding improve manufacturing and product consistency?
Bumper molding for cars supports mass production while maintaining stable quality.
Advantages:
High production efficiency
Injection molding enables fast, repeatable manufacturing cycles. For companies making thousands of units per day, this reduces lead time.
Consistency in dimensions
molds provide accurate shapes, ensuring each bumper fits the same model without manual adjustments.
Integration of functional features
Mounting points, grille openings, and reinforcement areas can be molded into the bumper in one step.
Expanded point:
For example, large automotive suppliers such as those working with global brands often rely on durable steel molds to produce plastic bumpers at high volumes. This stable output supports just-in-time manufacturing plans. Cars can move through the assembly line smoothly, avoiding delays caused by inconsistent part shapes. As a result, manufacturers control logistics more easily, which demonstrates how molding offers real operational benefits.
How does bumper molding support design and styling goals?
Automotive styling is a major selling point, and molded bumpers contribute significantly.
Advantages:
Flexible aesthetic shaping
Complex curves, textures, and details can be produced without excessive labor.
Compatibility with varied vehicle types
Sedans, SUVs, and commercial vehicles each require different bumper profiles; molding accommodates these variations.
Integration with modern materials
Lightweight thermoplastics help improve fuel economy and support aerodynamic body design.
Expanded point:
A popular SUV model may use a bumper with a prominent layered structure to enhance visual stability. The ability to mold such details helps automakers create distinct brand identities. In addition, textured finishes, such as matte grain patterns on certain pickup trucks, are achievable directly from the mold—reducing the need for post-processing. This shows how molding enhances both design creativity and manufacturing efficiency.
What practical benefits do molded bumpers provide for users?
Beyond aesthetics, molded bumpers affect daily driving experiences.
Advantages:
Light weight for easier vehicle control
Less mass contributes to responsive handling and gradual reduction in fuel consumption.
Improved pedestrian safety
Molded plastic materials generally deform more easily than metal during low-speed impacts.
Corrosion resistance
Plastic bumpers maintain structural appearance even in regions with rain or road salt.
Expanded point:
In many urban areas, drivers face frequent low-speed parking collisions. Molded bumpers, designed to absorb minor impacts while retaining shape, help reduce repair needs. Some models include energy-absorbing foam inserts behind the outer shell, enhancing protection for the vehicle structure. This indicates that molding supports practical functionality aligned with everyday usage.
What challenges and disadvantages still exist in bumper molding?
While useful, bumper molding is not free from issues that need attention.
Disadvantages:
Upfront mold cost is high
Creating precision molds requires specialized machining, which can be expensive for small production runs.
Plastic deformation under strong impact
In severe collisions, molded bumpers may crack or split, requiring full replacement.
Environmental concerns with disposal
Some plastics used in molding can be difficult to recycle efficiently without proper facilities.
Expanded point:
For instance, a new automobile start-up producing limited-edition vehicles might find mold investment burdensome because tooling costs are spread across fewer units. Additionally, although modern bumpers assist in protecting pedestrians, they may break more easily in high-energy crashes, higher replacement costs for drivers. As for sustainability, recycling programs differ from region to region, so molded bumper waste may still end up in landfills if proper separation and processing are unavailable.

 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666