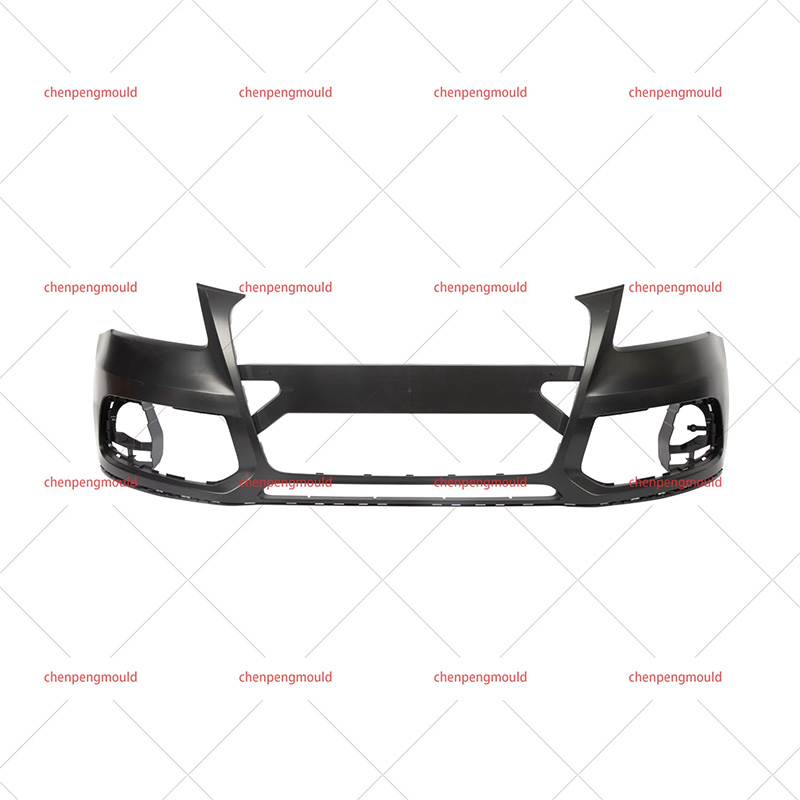
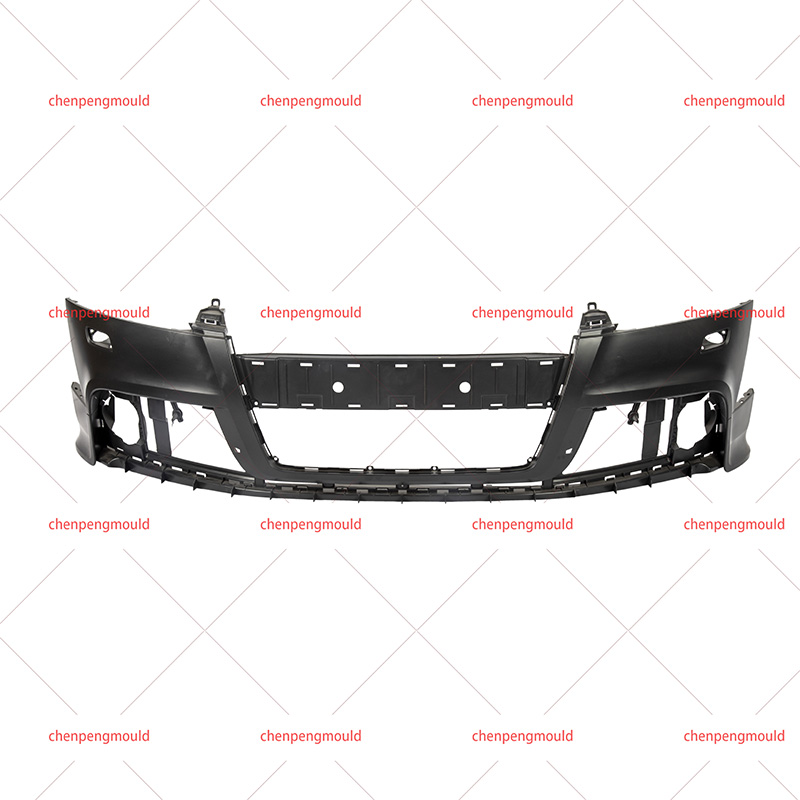
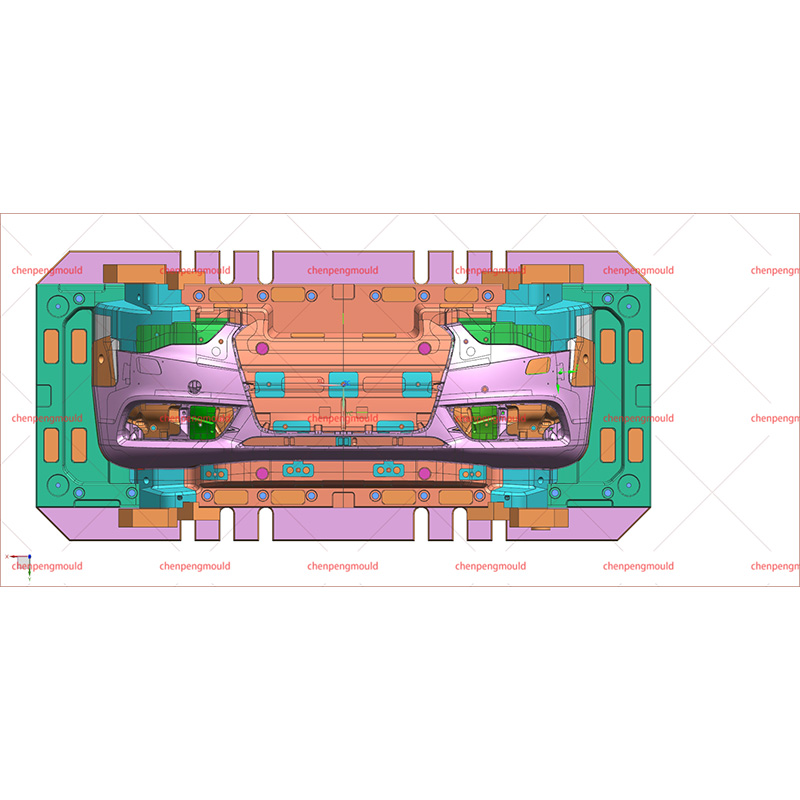
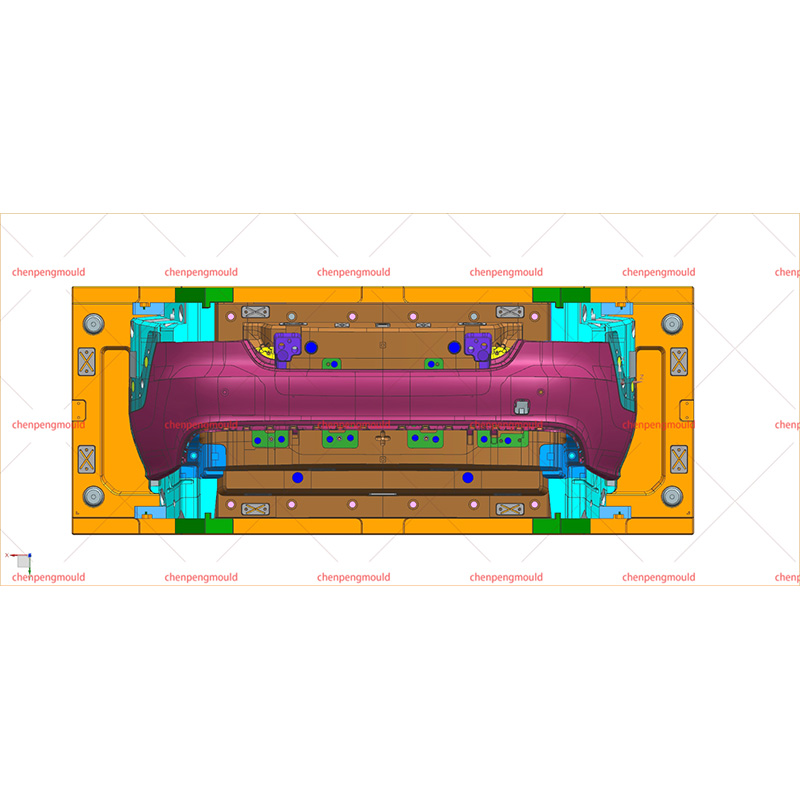
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Front Bumper Molding?
Material selection is one of the discussed topics in front bumper molding. Modern front bumpers are made from metal alone. Instead, manufacturers commonly use thermoplastic materials due to their balance of strength, flexibility, and weight reduction.
Polypropylene (PP), often reinforced with elastomers or glass fibers, is widely used because it offers good impact resistance and cost efficiency. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is another common material, valued for its dimensional stability and surface finish quality. In some applications, blends such as PC/ABS are used to achieve a balance between toughness and heat resistance.
The choice of material affects not only impact performance but also recyclability and manufacturing cost. As environmental regulations become more stringent, automakers increasingly prefer materials that support recycling and reduce overall vehicle weight, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
How Does Front Bumper Molding Affect Vehicle Safety?
Safety performance is a major public concern when discussing front bumper molding. The bumper is designed to absorb and distribute impact energy during low- to moderate-speed collisions, protecting both the vehicle structure and pedestrians.
Energy Absorption Design:
Molded bumpers often incorporate energy-absorbing structures such as ribs and honeycomb patterns. These features help dissipate collision forces more evenly.
Compatibility with Safety Systems:
Front bumper moldings must accommodate sensors for airbags, collision warning systems, and parking assistance. Accurate molding ensures proper alignment and sensor performance.
Pedestrian Safety Considerations:
Many modern bumper designs aim to reduce injury severity in pedestrian impacts by using flexible materials and controlled deformation zones.
The molding process must achieve consistent wall thickness and material distribution to ensure predictable performance under impact conditions.
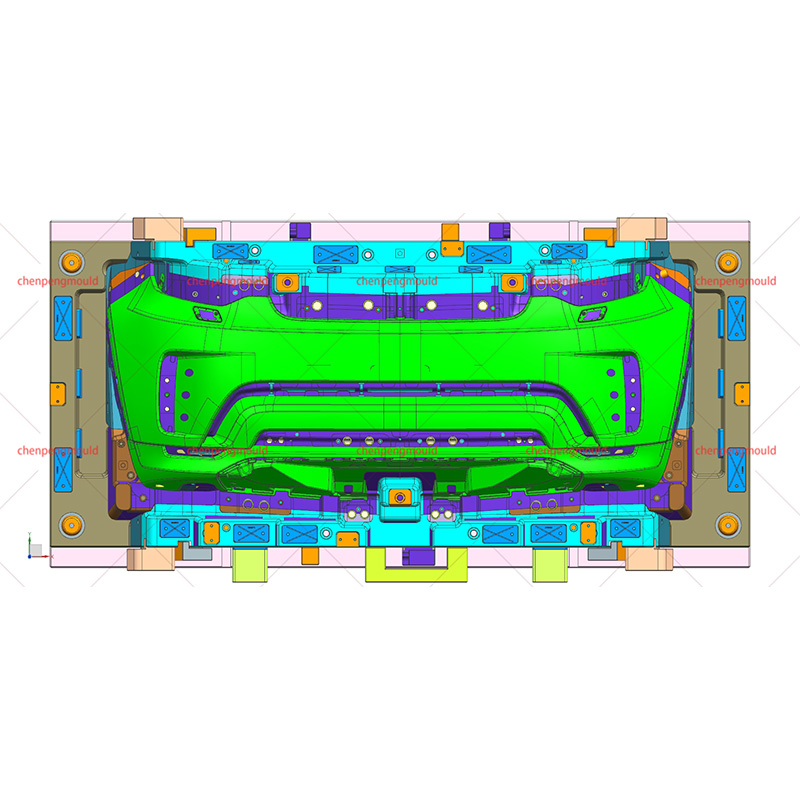
What Are the Key Manufacturing Challenges?
Front bumper molding presents several manufacturing challenges due to part size, complexity, and quality requirements.
Large Mold Size:
Front bumper molds are typically large and complex, requiring high-precision machining and robust mold bases.
Surface Quality Control:
Because the bumper is a visible exterior component, surface defects such as sink marks, weld lines, or flow marks must be minimized.
Dimensional Accuracy:
Tight tolerances are required to ensure proper fit with headlights, grilles, and body panels.
Process Stability:
Injection molding parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cooling time must be carefully controlled to avoid warping or internal stress.
These challenges make front bumper molding a process that demands advanced equipment, experienced technicians, and rigorous quality control.
How Do Cost and Customization Trends Influence Front Bumper Molding?
Cost control and customization are increasingly important considerations for both manufacturers and consumers. Automakers aim to balance production efficiency with the ability to offer different designs for various models and markets.
Customization often involves variations in styling, surface texture, or integration of decorative elements. This can be achieved through interchangeable mold inserts or secondary processing such as painting and coating. While customization adds value, it can also increase tooling and production costs.
From a cost perspective, manufacturers focus on optimizing mold design, reducing cycle time, and improving material utilization. Advanced simulation software is frequently used to predict material flow and cooling behavior, helping reduce defects and rework. Additionally, durable mold materials and proper maintenance can extend mold life and reduce long-term costs.
Balancing customization and cost requires careful planning in mold design and production strategy, particularly in high-volume automotive manufacturing.



 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666