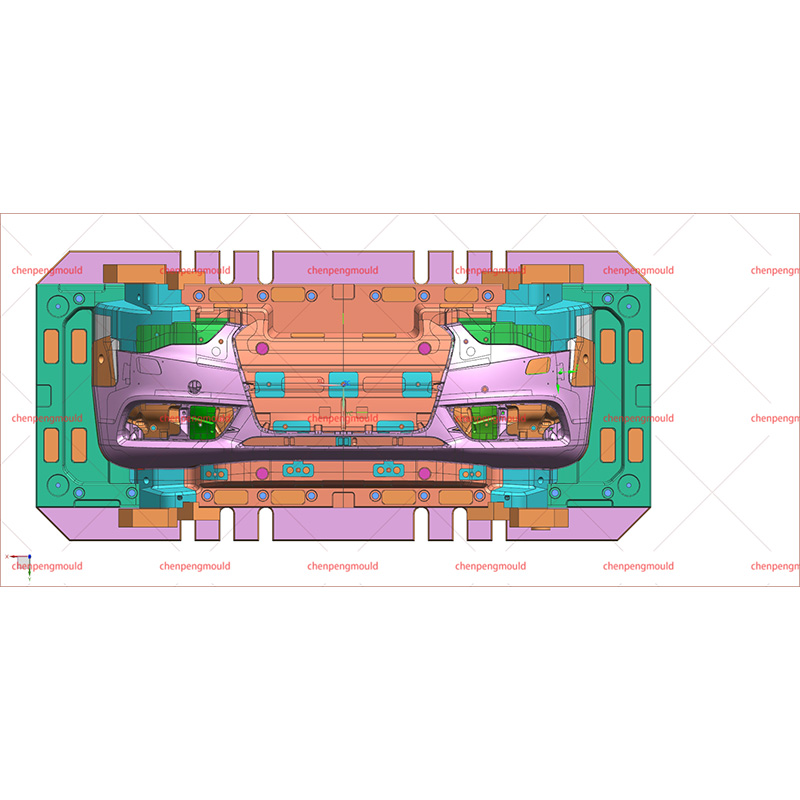
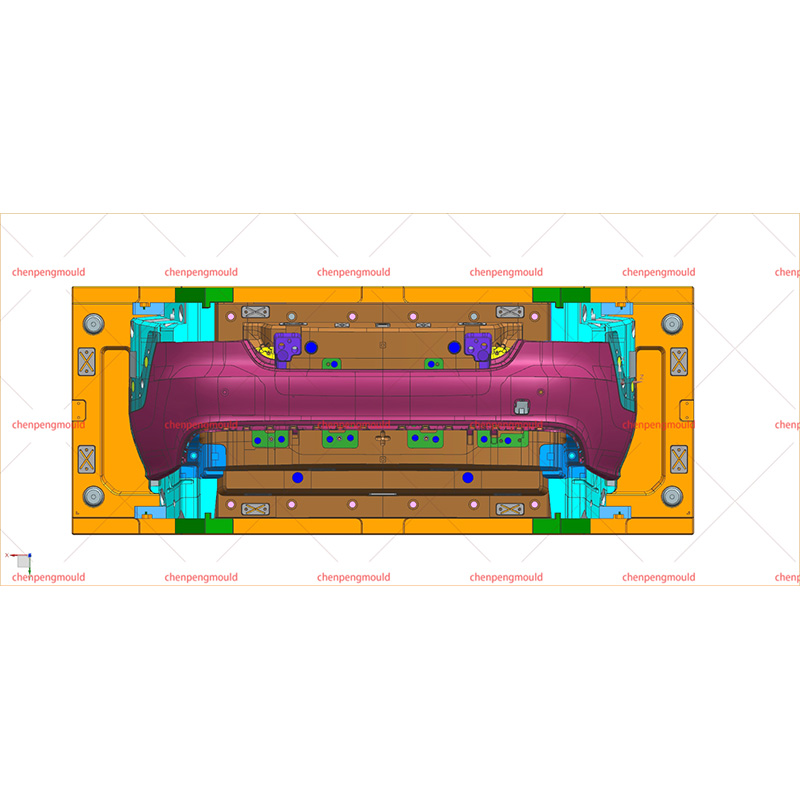
What Are the Drawbacks of Car Bumper Molding?
Car bumper molding is widely used in modern automotive manufacturing, but it has several practical limitations that should be understood objectively. One common drawback is the high initial tooling cost. Bumper molds are large, complex, and require precision machining, which bring about significant upfront investment. This cost can be a burden for small-volume production or frequent design changes.
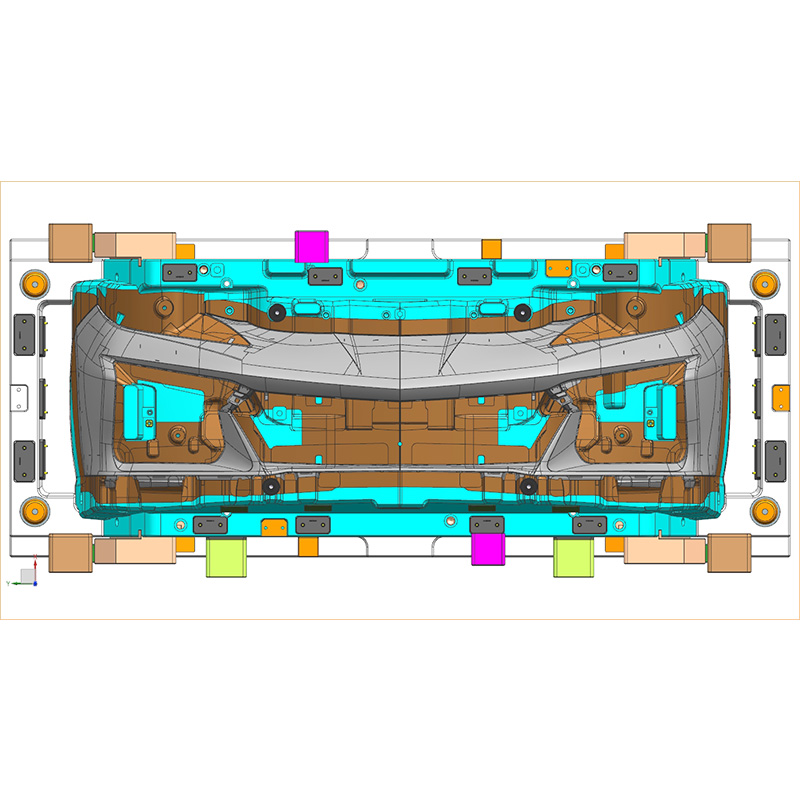
Another limitation relates to process sensitivity. Injection molding parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cooling time must be tightly controlled. Minor deviations can result in warpage, sink marks, or internal stress, which may affect dimensional accuracy and long-term durability. As front and rear bumpers are exterior components, even small surface defects can be unacceptable.
Material-related constraints also exist. While thermoplastics such as polypropylene and ABS offer good impact resistance and weight reduction, they may have limited heat resistance and aging performance compared with metal components. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation and temperature fluctuations can bring about fading or reduced toughness if material formulation and surface treatment are not properly managed.
Finally, recycling and repair can be challenging. Multi-material designs and painted surfaces complicate recycling processes, while damaged molded bumpers are often replaced rather than repaired, increasing maintenance costs for vehicle owners.
How to Correctly Understand Car Bumper Molding?
To understand car bumper molding accurately, it is important to view it as a system-level manufacturing process rather than a single forming step. The following points provide a structured perspective:
Integration of Design and Function
Bumper molding is not only about appearance. The molded part must integrate energy absorption structures, mounting features, and space for sensors, all within limited dimensional tolerances.
Material Selection Is Application-Driven
Different vehicles require different material formulations. Factors such as impact standards, climate conditions, and weight targets influence whether PP, modified PP, or blended plastics are selected.
Tooling Quality Determines Product Consistency
High-quality mold design and manufacturing are essential. Proper gate location, cooling channel layout, and venting directly affect surface finish and structural integrity.
Process Control Is Central to Performance
Stable injection molding conditions ensure consistent wall thickness and predictable mechanical behavior. Automation and monitoring systems are often used to reduce variability.
Compliance With Regulations Matters
Bumper molding must meet safety, environmental, and recyclability regulations in different markets. These requirements influence both design and material choice.
Lifecycle Perspective Is Necessary
Understanding bumper molding includes considering durability, repairability, and end-of-life handling, not just initial production.
By viewing car bumper molding through these interconnected factors, its role in modern vehicle manufacturing becomes clearer and more realistic.
Design Considerations in Car Bumper Molding
Car bumper molding design focuses on balancing structural performance, aesthetics, and manufacturability. One key consideration is wall thickness uniformity. Consistent thickness helps reduce internal stress and prevents defects such as sink marks or warping during cooling. Designers often use rib structures to reinforce strength without adding excessive material.
Another important aspect is integration with other vehicle components. The bumper must align precisely with headlights, grilles, and body panels. Mounting points and clips are molded directly into the part, requiring accurate dimensional control. Additionally, modern bumpers must accommodate sensors for parking assistance and collision detection, which places further constraints on design layout.
Surface quality is also a major consideration. Since bumpers are visible exterior parts, mold surface finish and material flow behavior must support smooth, paint-ready surfaces. Texture design may be used to reduce the visibility of minor scratches or wear over time.
Manufacturing and Quality Control Factors
Manufacturing car bumper molding involves large-scale injection molding equipment and strict quality management. Due to the size of bumper components, uniform cooling is difficult to achieve, making cooling system design within the mold especially important. Uneven cooling can bring about deformation or dimensional instability.
Quality control typically includes dimensional inspection, visual surface checks, and mechanical testing. Automated inspection systems are increasingly used to detect defects early in the production cycle. Process documentation and traceability help manufacturers identify the root causes of defects and maintain consistent output.
Maintenance of molds is another critical factor. Regular cleaning, inspection, and repair extend mold life and help maintain consistent part quality over long production runs. Without proper maintenance, wear and corrosion can compromise surface finish and dimensional accuracy.


 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666