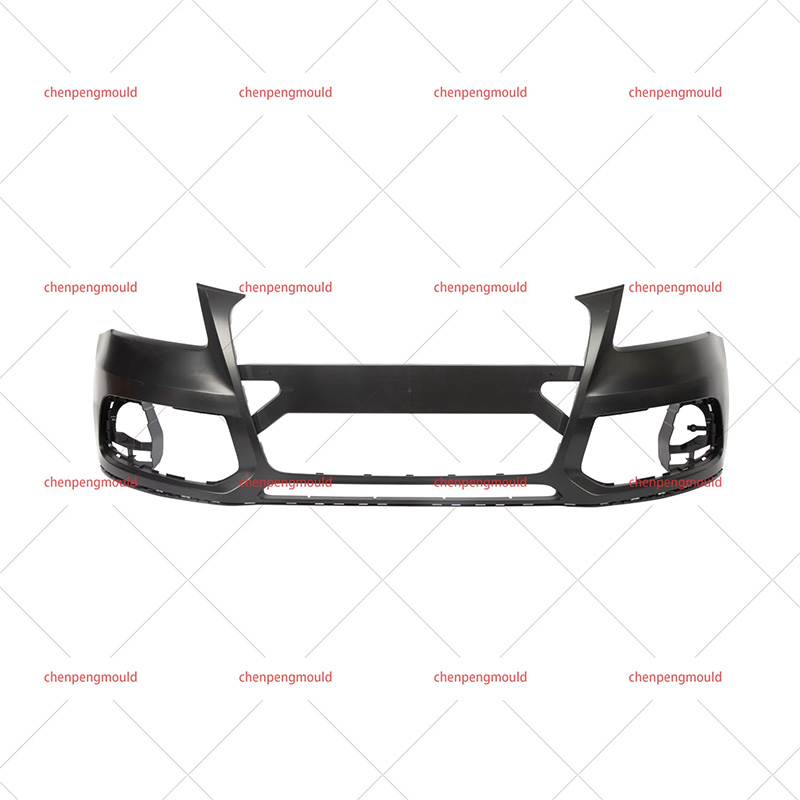
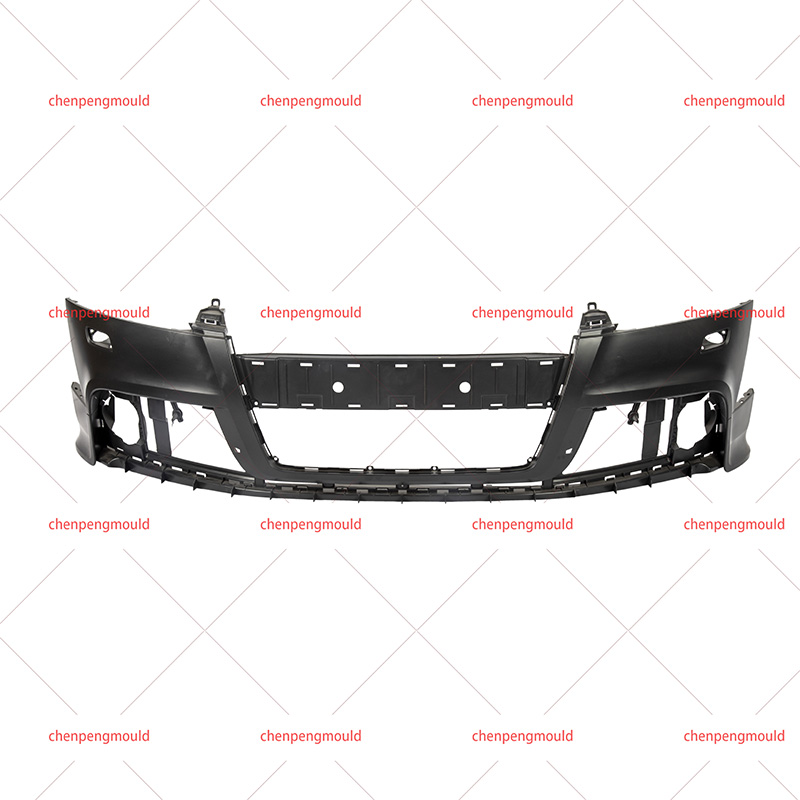
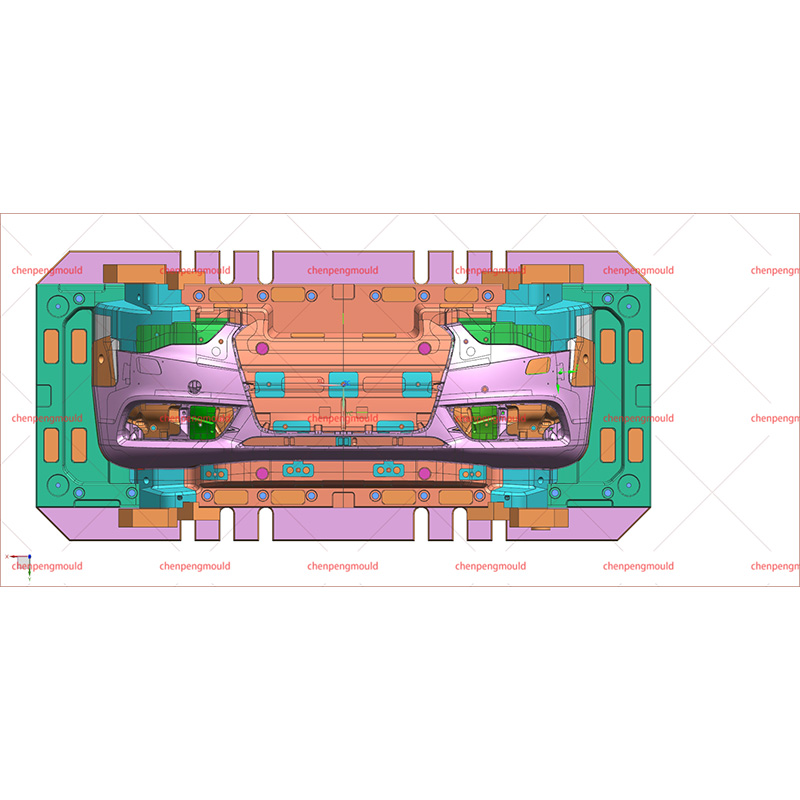
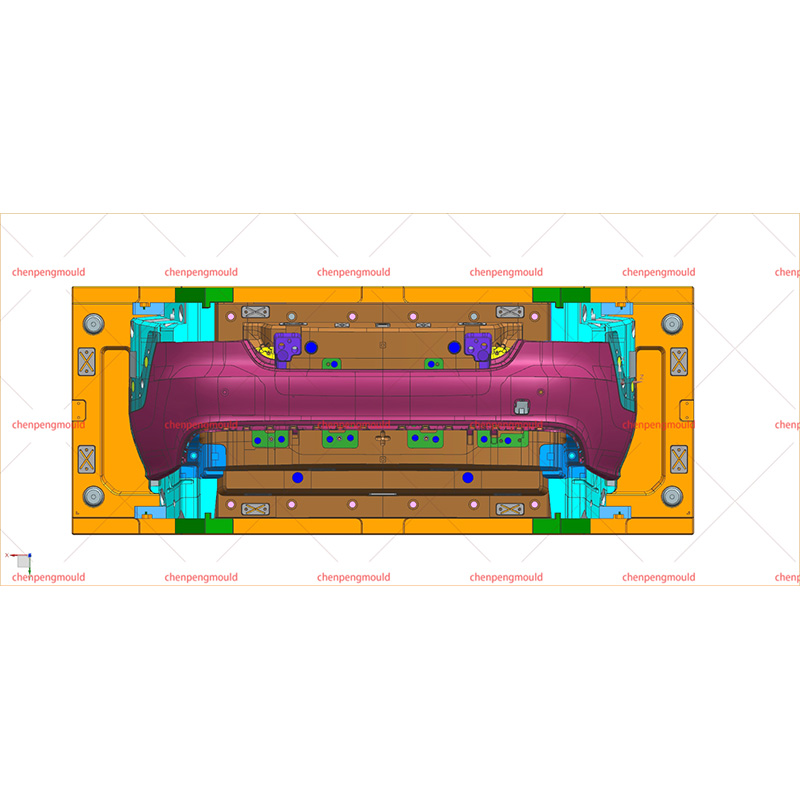
Types of Automotive Parts Molds
There are various types of molds used in the automotive industry, each tailored to specific manufacturing methods and parts. The common types include:

Injection Molds: These molds are used in the injection molding process, where molten plastic or metal is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. Injection molds are frequently used for parts such as dashboard components, trim pieces, and small plastic clips. The injection molding process is ideal for producing high volumes of small to medium-sized parts with intricate details.
Compression Molds: In compression molding, materials like rubber or composite materials are placed into a mold cavity and then compressed using heat and pressure. This process is commonly used for creating parts such as seals, gaskets, and various rubber components used in the automotive industry.
Die Cast Molds: These molds are used in the die-casting process, where molten metal is injected into a mold under high pressure to create automotive components like engine blocks, gearbox housings, and transmission parts. Die cast molds are made of high-strength alloys to withstand the pressures involved in the casting process.
Blow Molds: Blow molding is a process used to create hollow parts, such as fuel tanks, air ducts, and other fluid-handling components. The process involves inflating a hot plastic tube inside a mold to create the desired shape. Blow molds are commonly used in producing parts that require both durability and a hollow structure.
The Importance of Precision in Automotive Molds
Precision is a critical factor in the design and production of automotive parts molds. Each automotive part must meet strict tolerances to ensure it fits seamlessly with other components in the vehicle. Even small deviations in size or shape can cause issues during the assembly process, bring about increased manufacturing costs and potential safety concerns.
To achieve the necessary precision, automotive molds are designed using advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software and manufactured with machinery. Molds are often tested and adjusted during production to ensure that they meet the exact specifications required. The quality of the mold itself directly impacts the quality of the final automotive part. A well-designed mold reduces the likelihood of defects, such as air bubbles, material inconsistencies, or dimensional errors, that can compromise the functionality and safety of the part.
The Role of Material Selection in Molding Process
The material used for both the mold and the parts being molded plays a significant role in the overall success of the automotive molding process. Mold materials are typically selected for their strength, durability, and heat resistance, as they need to withstand the high temperatures and pressures during the molding process. For example, steel is a popular choice for injection and die-casting molds due to its toughness and resistance to wear.
For the molded parts themselves, the selection of materials depends on factors like strength, weight, heat resistance, and durability. Automotive parts are often made from a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, composites, and rubber. For example, lightweight thermoplastics might be used for interior parts to reduce overall vehicle weight, while metals such as aluminum or magnesium alloys are chosen for structural parts due to their strength and resistance to heat.
The correct combination of mold material and part material is essential to ensure the desired characteristics of the final product, such as strength, appearance, and ease of assembly.
Common Challenges in Automotive Parts Molding
Design Complexity
The design of automotive parts and molds can be highly complex. Modern vehicles often require parts with intricate geometries or specific performance characteristics, such as resistance to heat or flexibility. Designing molds to produce these parts with high precision can be a challenging task. The mold must be able to handle the pressure and temperature of the manufacturing process while maintaining the desired part specifications.
Tooling Costs and Time
Molds, especially those used for high-volume production, can be expensive to produce. The initial design, prototyping, and testing phases can be time-consuming and costly, but they are necessary to ensure that the mold performs as required. As automotive parts are often produced in large quantities, the cost of tooling can be spread out over many units, but it is still a significant investment. The time taken to produce the mold must also be accounted for, as delays in mold production can bring about longer lead times for the overall vehicle manufacturing process.
Material and Process Compatibility
Another challenge in automotive parts molding is ensuring that the materials used for the part and the mold are compatible with each other and the manufacturing process. For instance, if the material for the part is not able to withstand the temperature and pressure of the mold, defects such as warping or cracking can occur. Additionally, the mold material must be carefully selected to match the type of molding process being used. The failure to select the correct materials can bring about problems such as tool wear, excessive cycle times, or part defects.

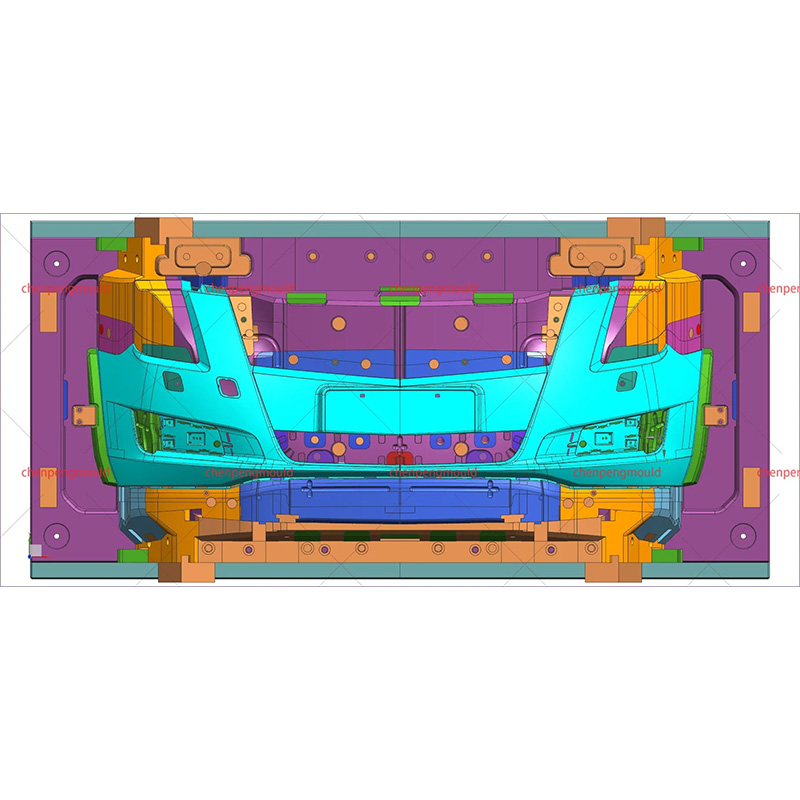
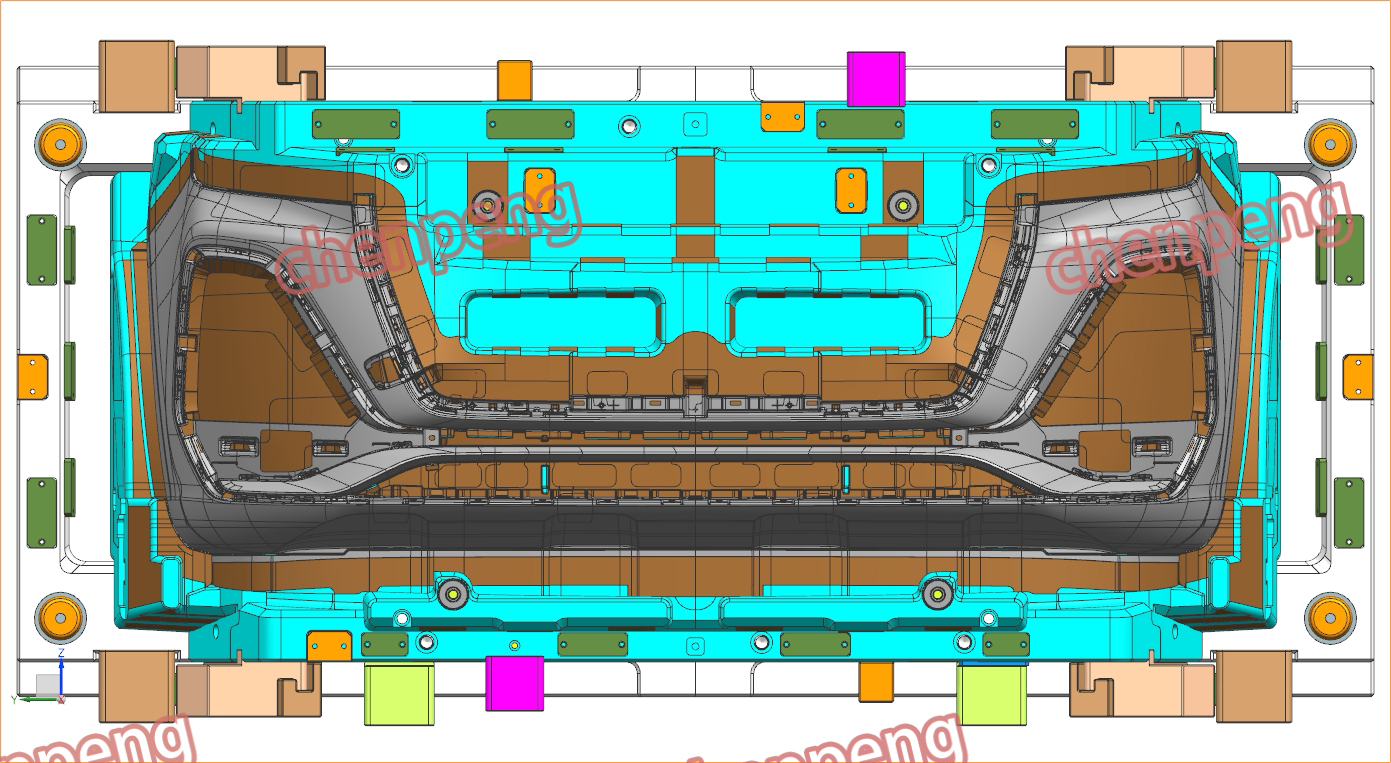
 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666