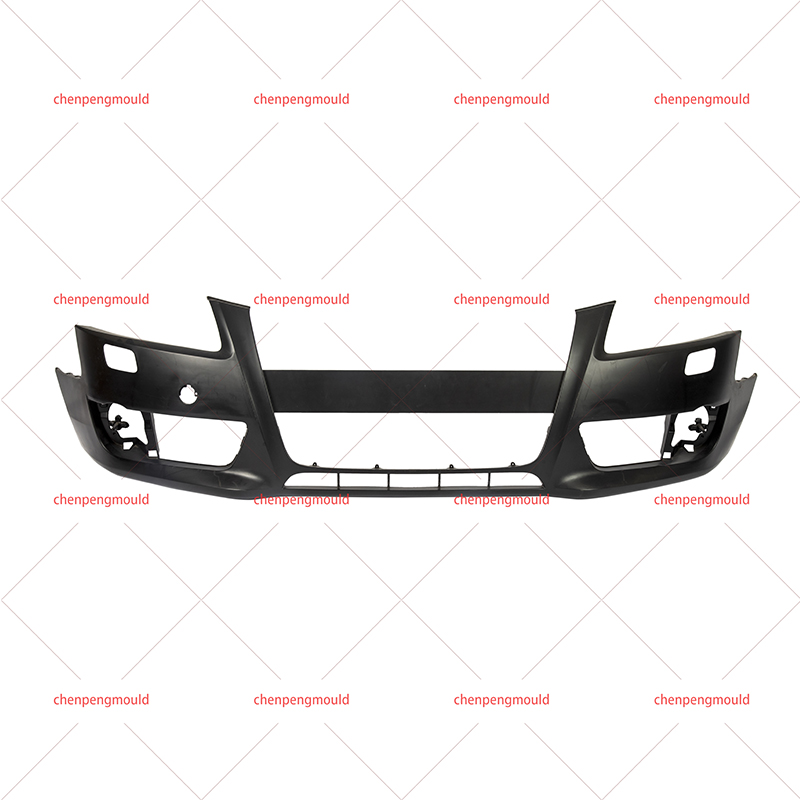
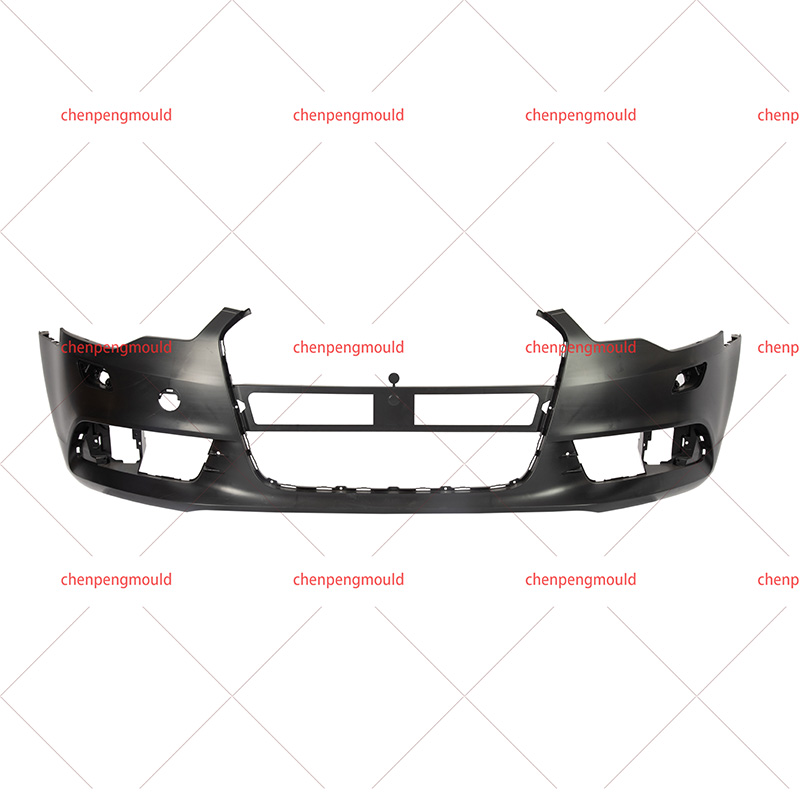
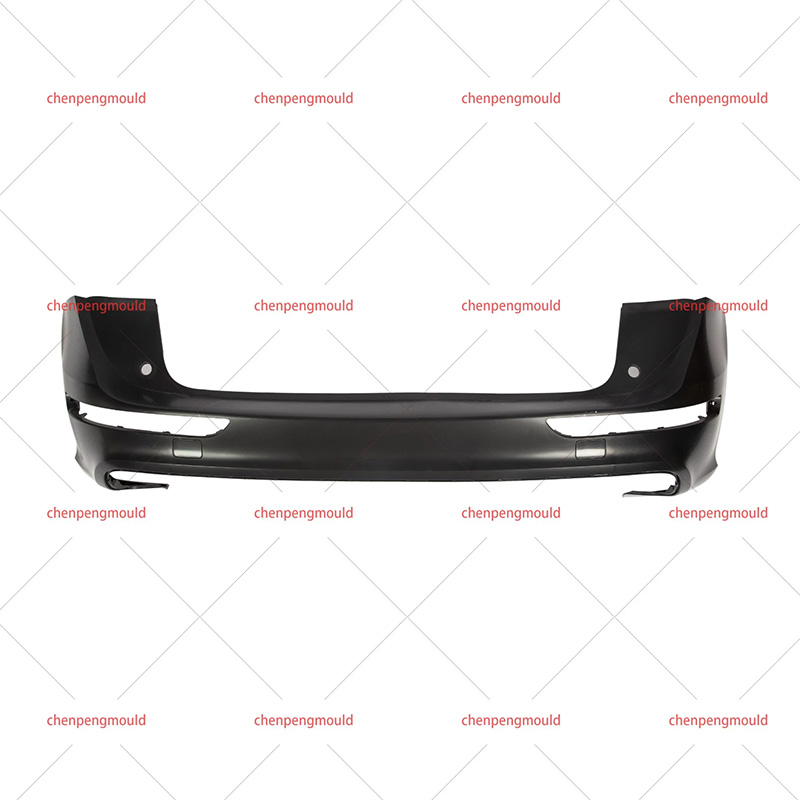
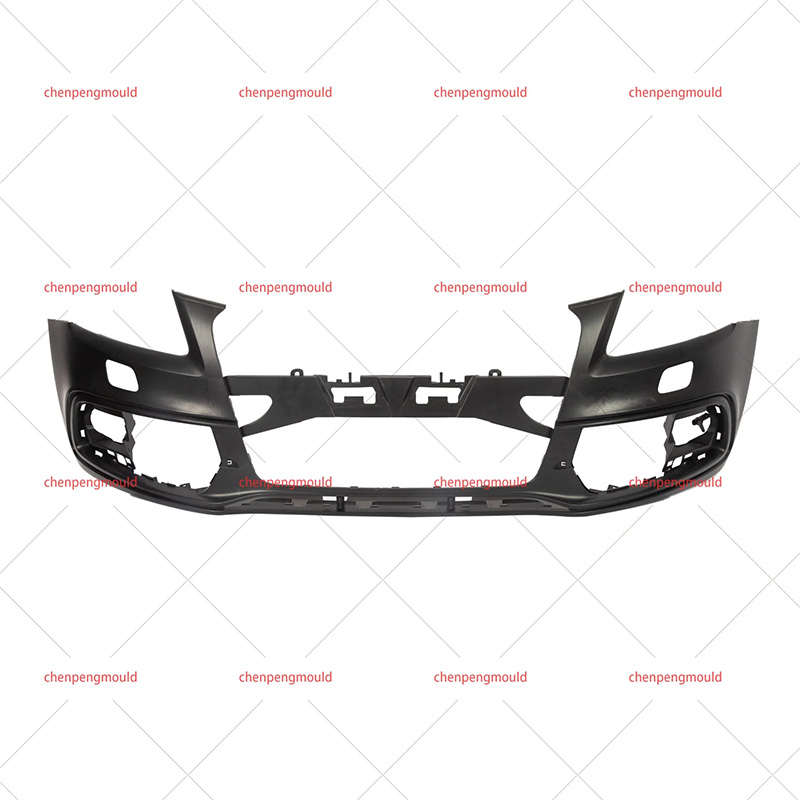
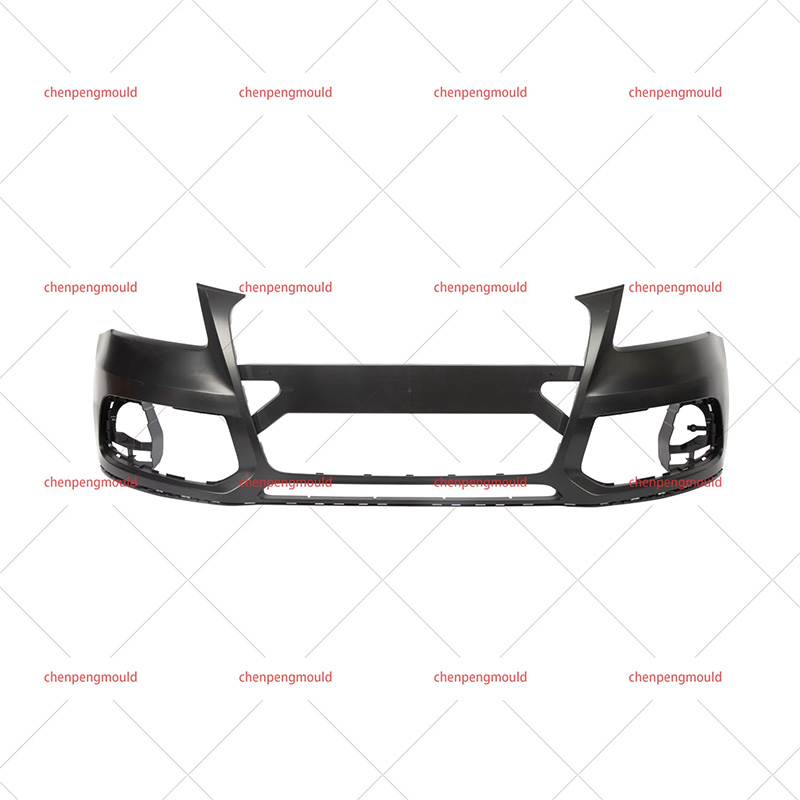
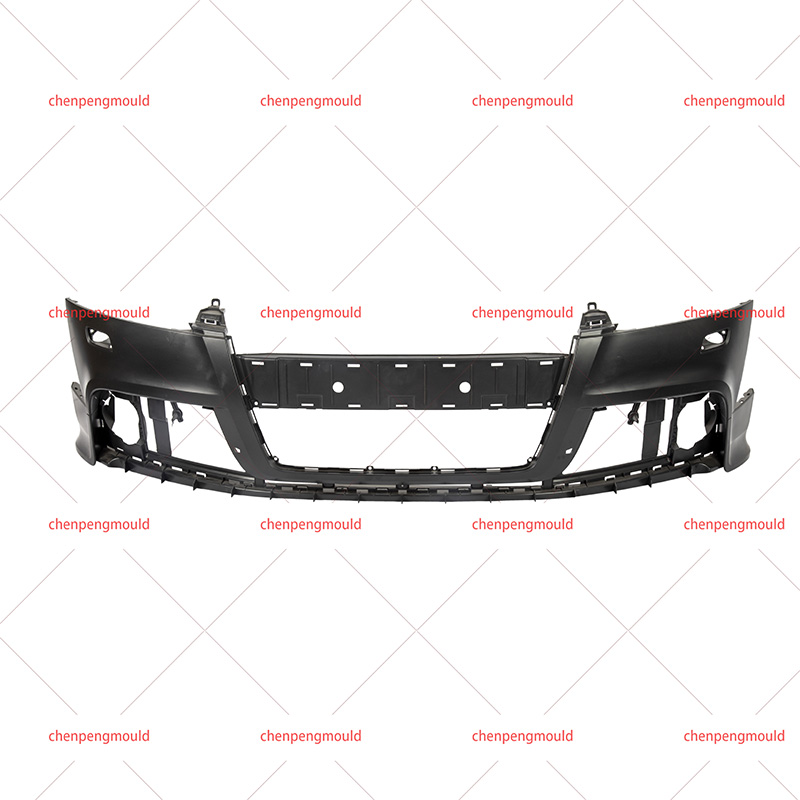
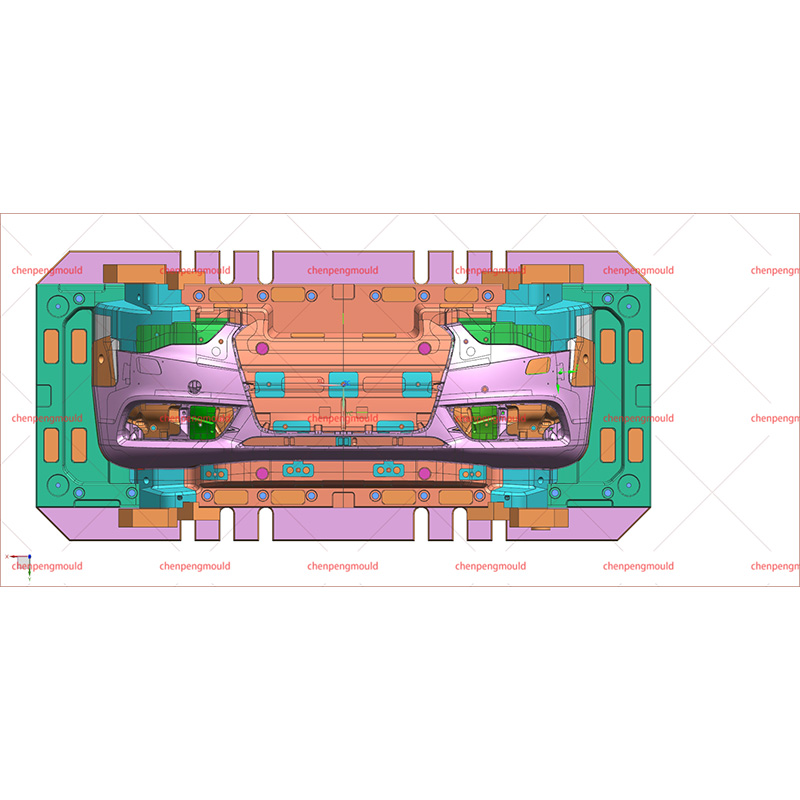
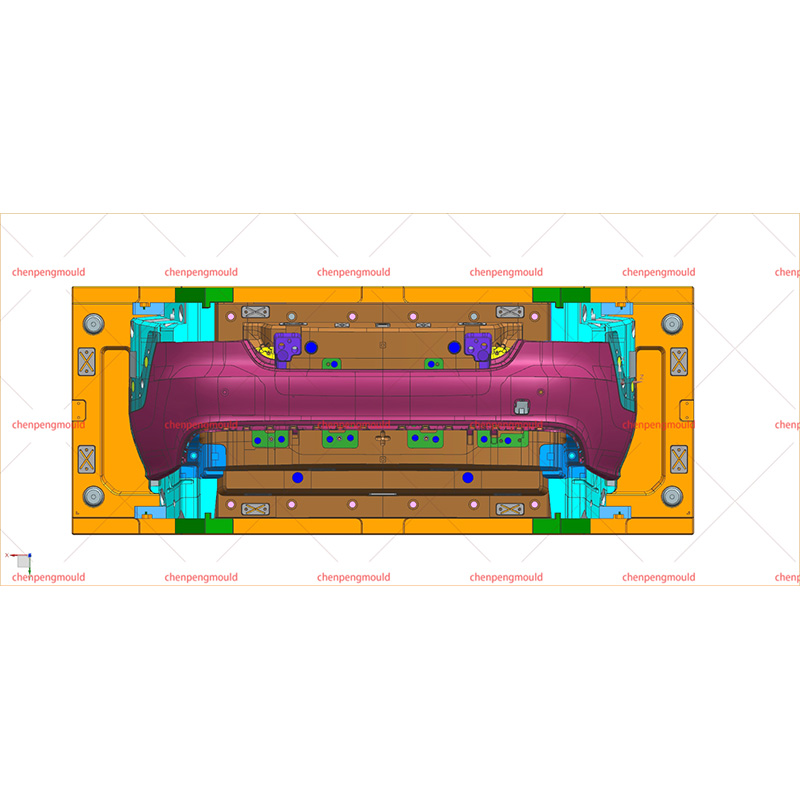
Plastic bumper moulds are essential tools used in the manufacturing of vehicle bumpers. They play a critical role in shaping and forming bumpers made from plastic materials, ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications for strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. With the increasing demand for lightweight, high-performance, and environmentally-friendly materials, plastic bumper moulds have evolved to meet the latest manufacturing standards.
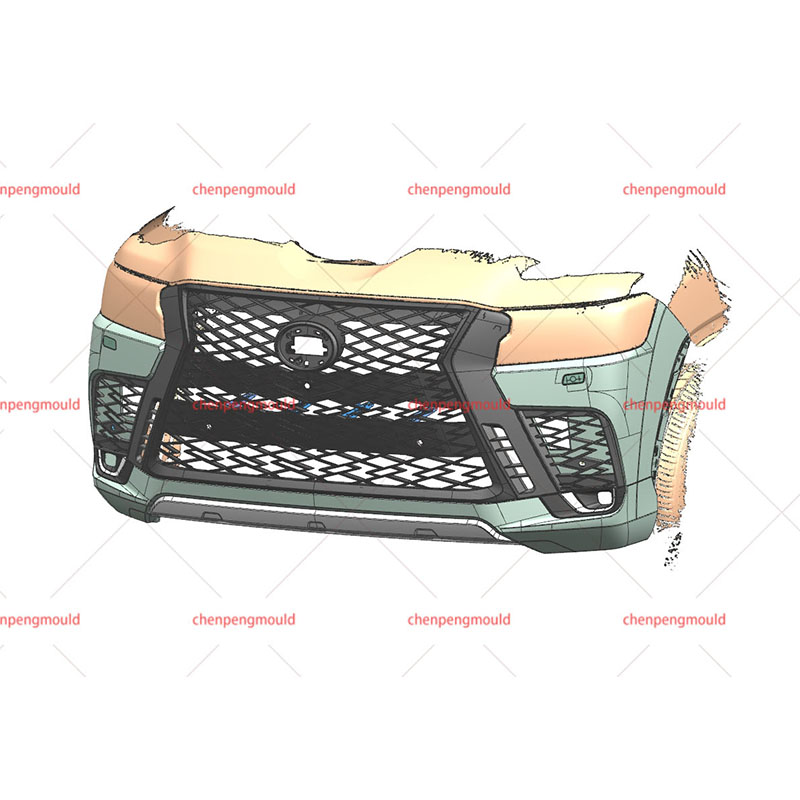
1. What is a Plastic Bumper Mould?
Plastic bumpers are used in vehicles primarily for protection in the event of minor collisions. These bumpers are often made from materials that provide the right balance of flexibility and strength to absorb impact while maintaining the aesthetic look of the vehicle.
2. Materials Used in Plastic Bumper Moulds
The materials used to make plastic bumper moulds are crucial for their ability to withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved in the injection moulding process. The primary materials used for plastic bumper moulds are metals that offer durability and heat resistance. These materials include:
a. Steel
Steel is the commonly used material for plastic bumper moulds due to its strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. Steel moulds can withstand the high temperatures and pressures associated with the injection moulding process, making them ideal for producing high-quality bumpers.
Advantages of Steel Moulds:
Durability: Steel is highly resistant to deformation and wear, making it suitable for producing large volumes of bumpers.
Heat Resistance: Steel can withstand the high temperatures needed for injection moulding without losing its structural integrity.
Strength: Steel moulds are strong enough to withstand the pressures generated during the moulding process.
Disadvantages of Steel Moulds:
Cost: Steel moulds are generally more expensive than other options, especially for initial production runs.
Weight: Steel is heavier than other materials, which can increase the overall weight of the mould and affect its handling during production.
b. Aluminum
Aluminum is another popular material for plastic bumper moulds, particularly in cases where faster production times and lower costs are priorities. Aluminum moulds are lighter than steel moulds and offer good thermal conductivity, which helps with the cooling process after the plastic has been injected into the mould.
Advantages of Aluminum Moulds:
Cost-Effective: Aluminum is generally more affordable than steel, making it a good choice for lower-volume production runs.
Lighter Weight: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easier to handle and transport during production.
Good Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum cools more quickly than steel, helping to reduce cycle times and improve productivity.
Disadvantages of Aluminum Moulds:
Lower Durability: Aluminum is softer than steel and is more susceptible to wear and tear over time.
Limited Lifespan: Aluminum moulds may need to be replaced more frequently than steel moulds due to the lower resistance to damage.
c. Hardened Steel
Hardened steel moulds are a step above regular steel moulds in terms of durability and wear resistance. These moulds are often used for high-precision applications where a longer lifespan is essential. Hardened steel is ideal for producing bumpers in high volumes because it can withstand the stresses of repeated use without significant degradation.
Advantages of Hardened Steel Moulds:
Longer Lifespan: Hardened steel is more resistant to wear and tear, extending the lifespan of the mould.
High Precision: The material allows for greater accuracy in the moulding process, ensuring that the bumpers meet tight tolerance specifications.
Disadvantages of Hardened Steel Moulds:
High Cost: The process of hardening steel makes these moulds more expensive to produce.
Machining Difficulty: Hardened steel is harder to machine, which can make the initial fabrication process more time-consuming and costly.

 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666