The automotive industry is known for its precision and complexity, with each part of a vehicle requiring exacting standards of manufacturing. One of the key elements in the production of automotive components is the use of automotive moulds. These moulds are essential in creating a wide variety of car parts, from body panels to engine components. But what exactly does an automotive mould include?

Overview of Automotive Moulds
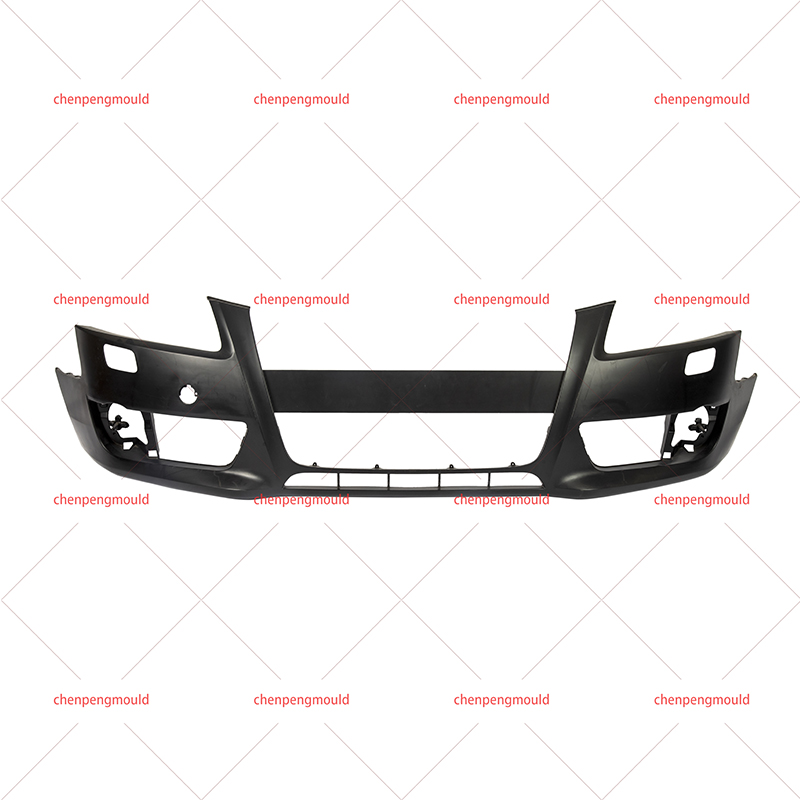
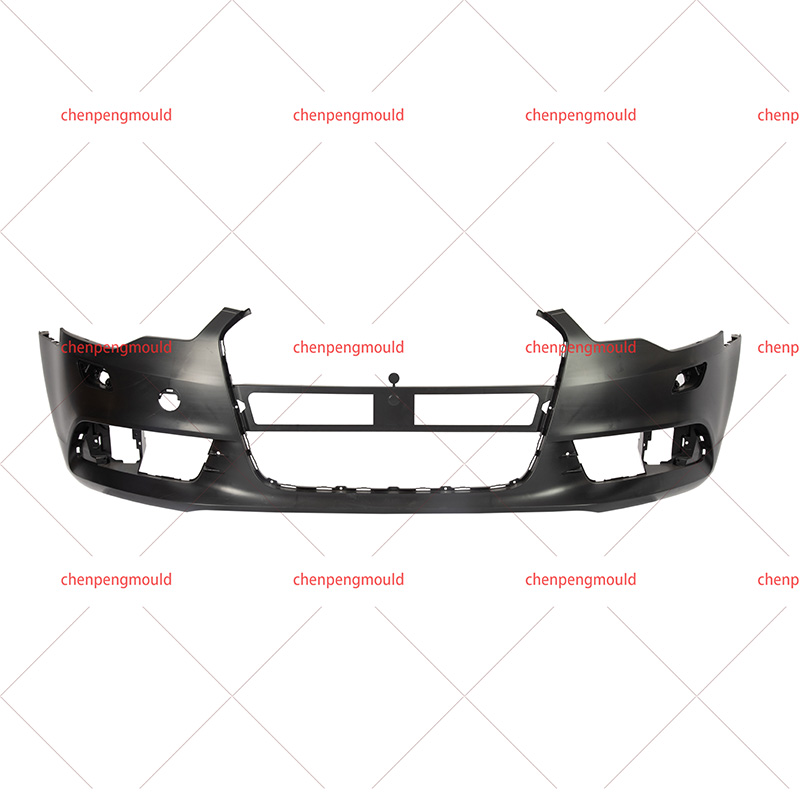
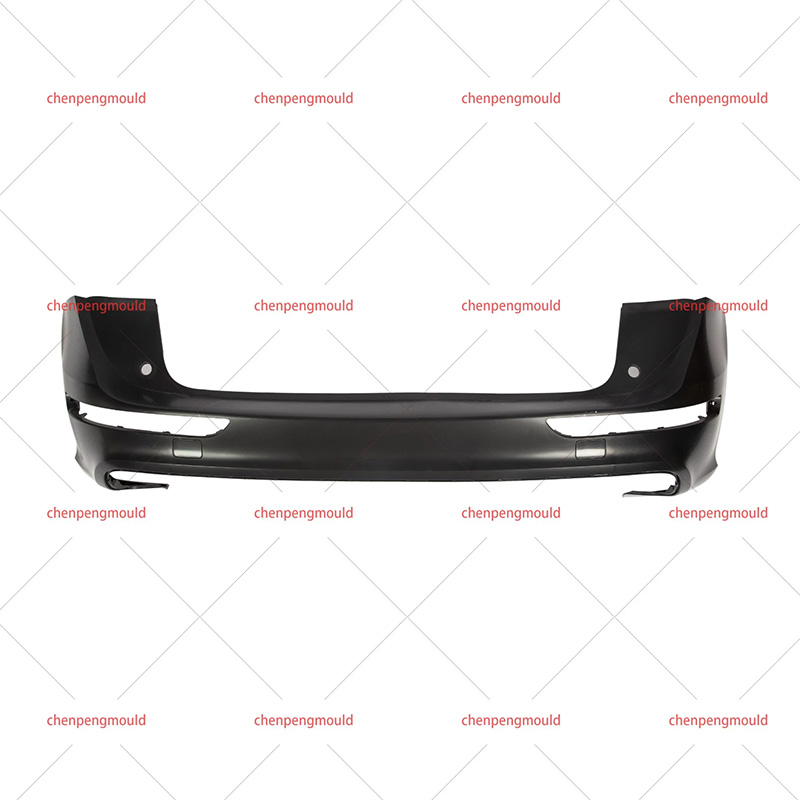
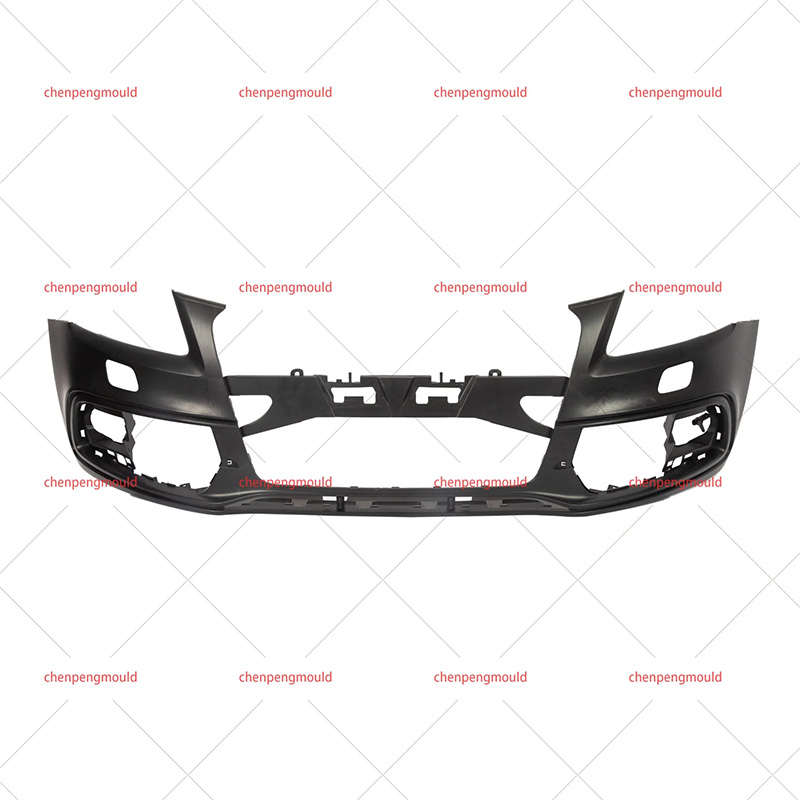
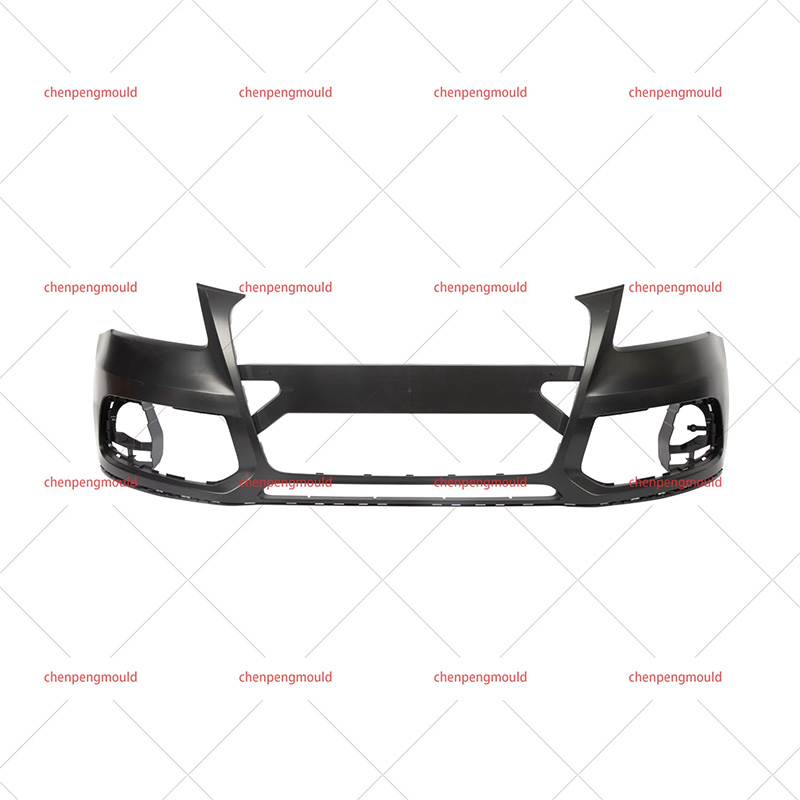
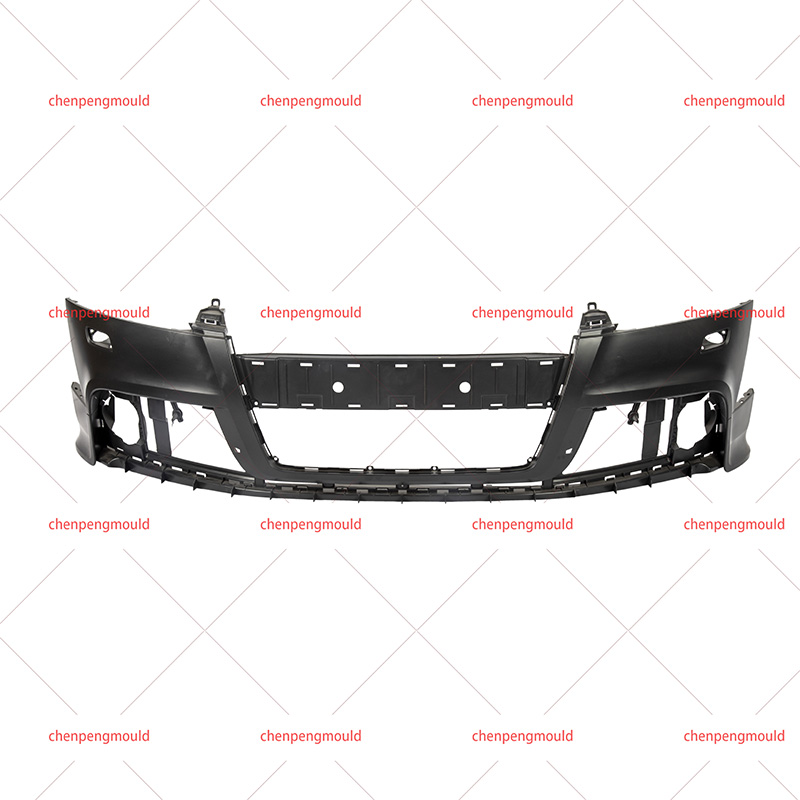
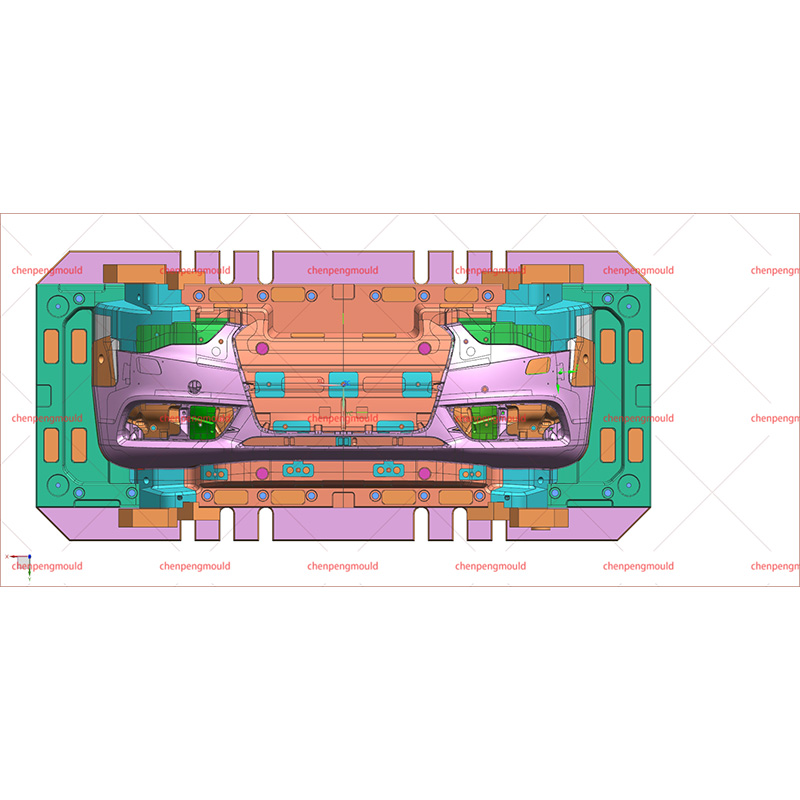
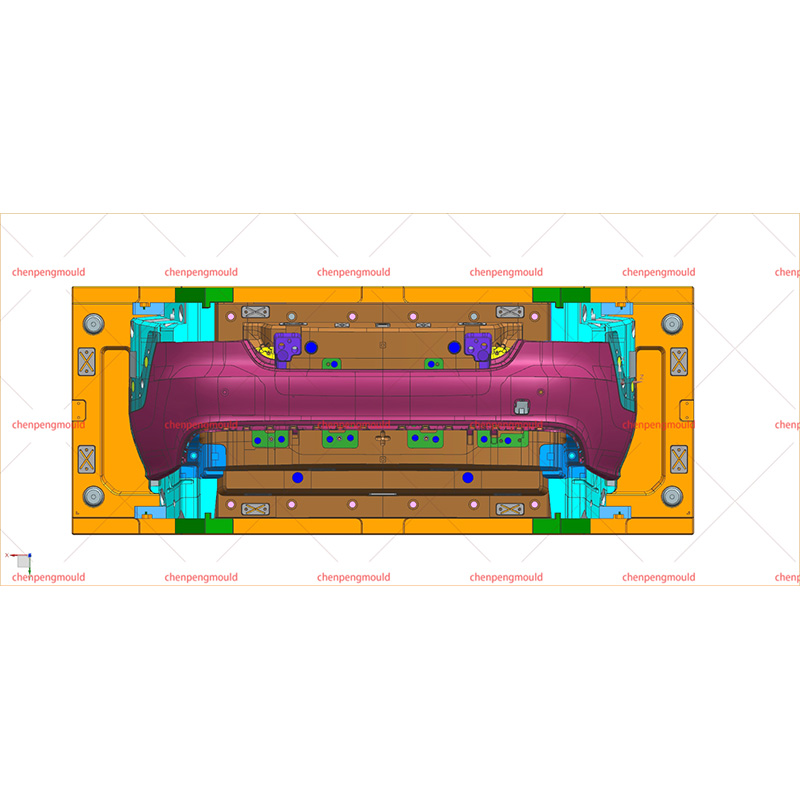
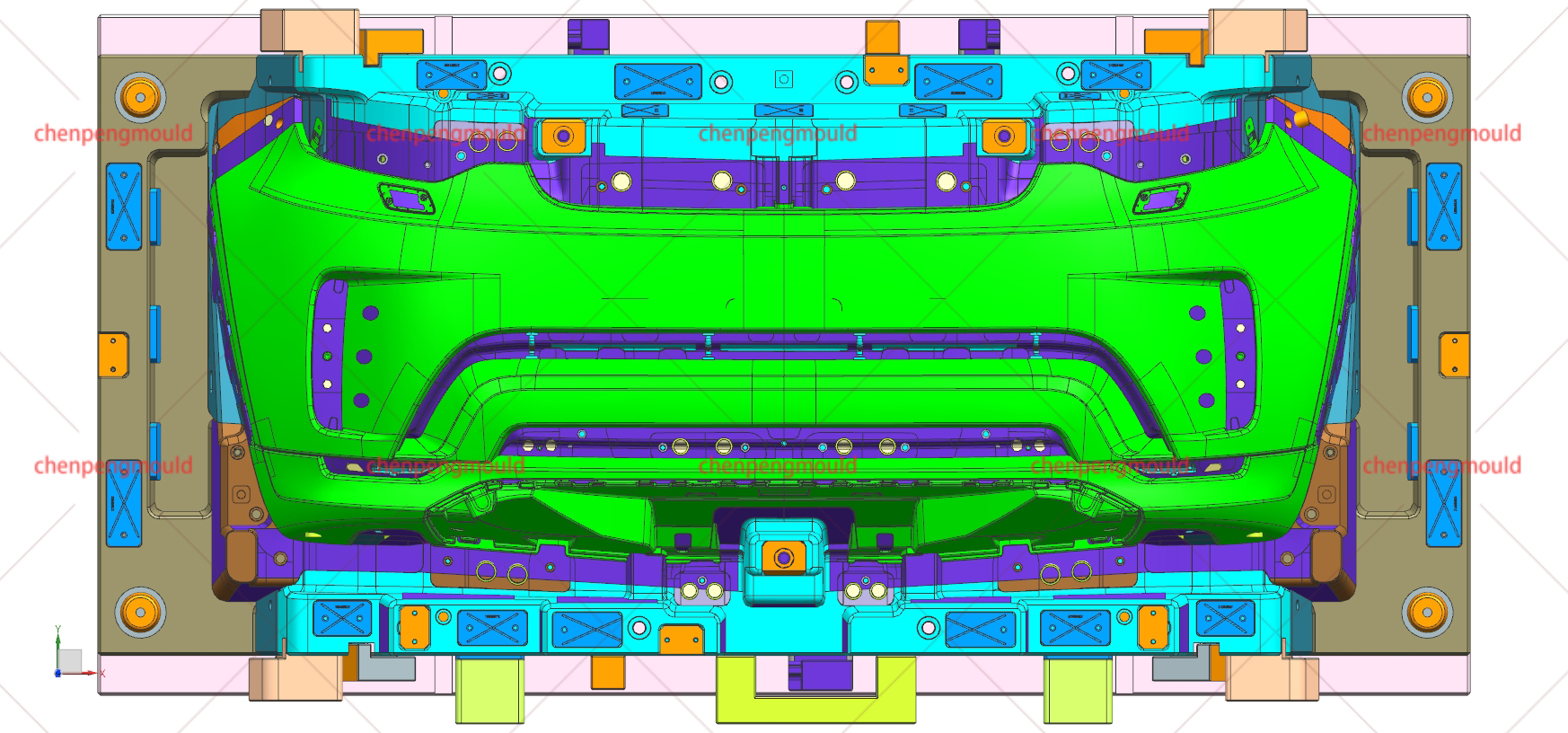
An automotive mould is a specialized tool used to shape and form parts used in the automotive industry. These moulds are typically made of high-quality materials capable of withstanding the pressures, temperatures, and repetitive processes involved in car part production. Automotive moulds are used for producing everything from small interior components to large exterior parts, including bumpers, dashboards, door panels, and engine covers.
These moulds are generally created through injection moulding, compression moulding, or die-casting techniques, depending on the material being used and the part's requirements.
Mould Core and Cavity
At the core of every automotive mould are the core and cavity components. These two parts are essential for creating the desired shape of the component.
Core: The core is the internal part of the mould that creates the inner surface of the part. For example, in a bumper mould, the core shapes the inside of the bumper. It is often made from hardened steel or other durable materials to resist wear and high temperatures during the production process.
Cavity: The cavity is the external part of the mould that forms the outer surface of the automotive part. It is equally important as the core in ensuring that the exterior dimensions of the part meet the specifications required by the design.
Both the core and cavity must be precisely designed and engineered to create high-quality automotive parts. They work together to create a replication of the intended product.
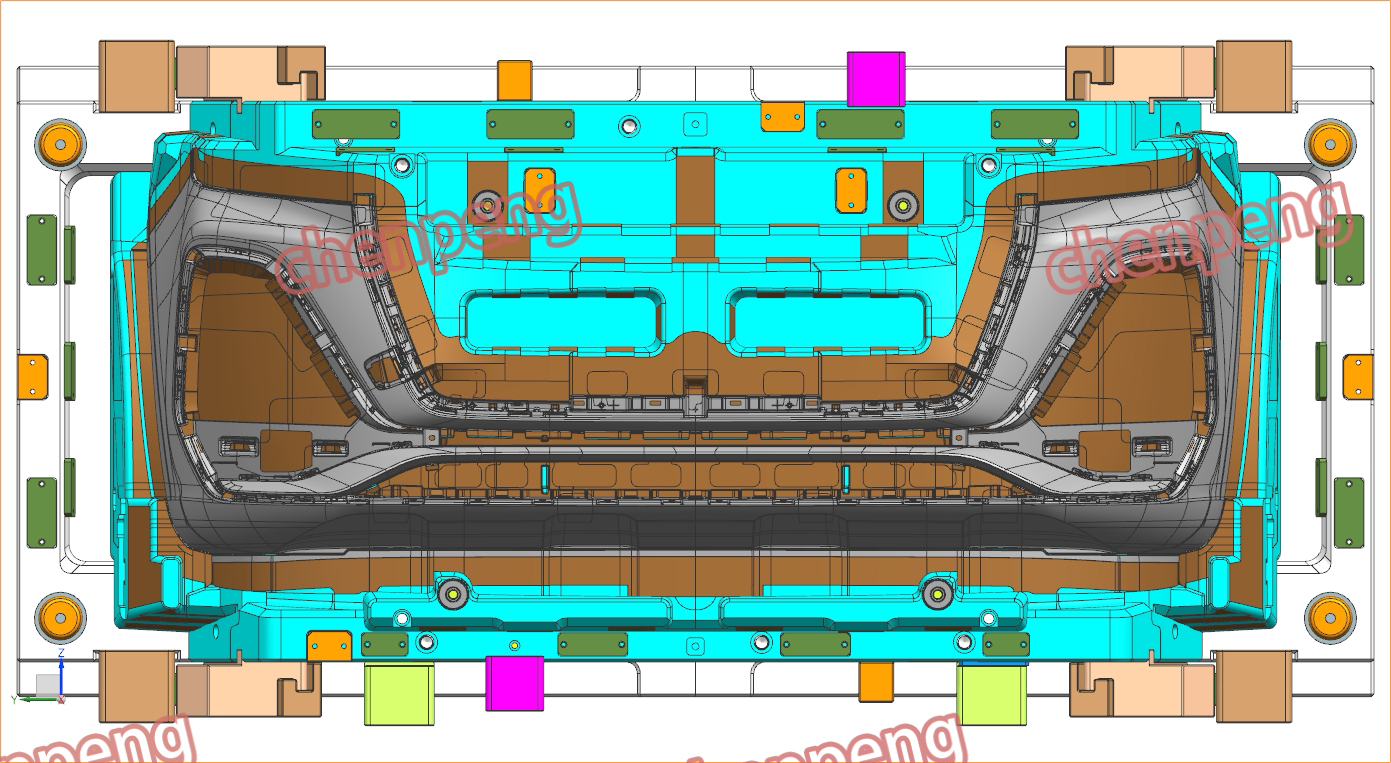
Mould Base
The mould base serves as the foundation for the core and cavity. It holds all the components of the mould together and provides the necessary structural support to withstand the high pressures and forces exerted during the manufacturing process. The base is typically made from strong metals such as steel or aluminum. These materials are chosen for their strength and ability to maintain the integrity of the mould under various operating conditions.
In addition to providing structural support, the base often includes cooling and heating channels. These channels help regulate the temperature of the mould, ensuring that the material inside solidifies correctly and preventing warping or deformation of the final part.
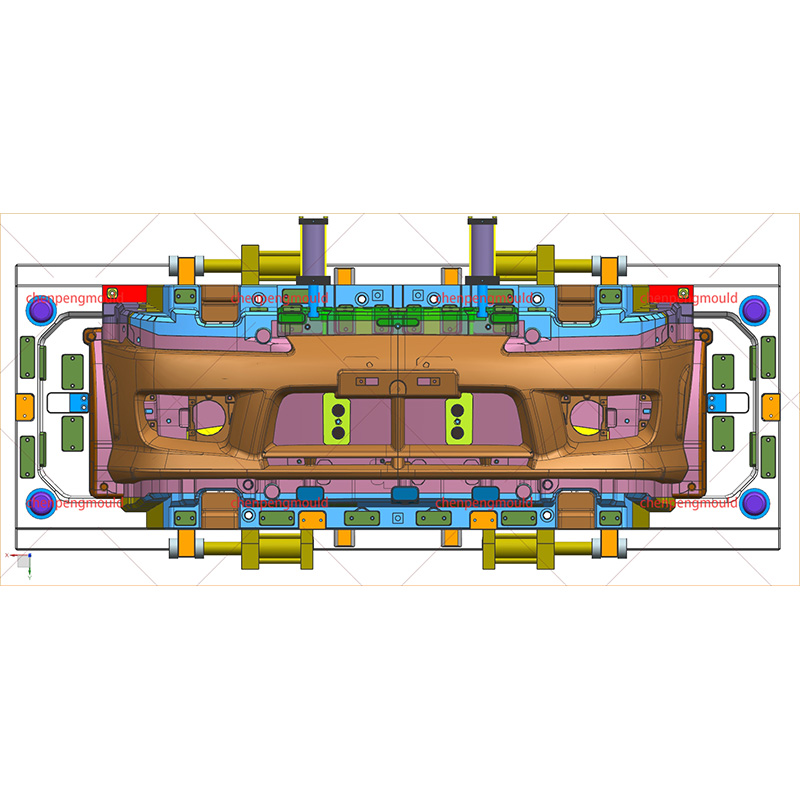
Ejector System
One of the key aspects of an automotive mould is the ejector system. This system is responsible for removing the finished part from the mould after the material has cooled and solidified. Typically, the ejector system consists of pins, sleeves, or plates that push the component out of the mould cavity.
The ejector system must be carefully designed to avoid damaging the newly formed part. Additionally, it needs to operate efficiently to ensure a smooth production process, the time taken to extract each component and allowing for high throughput in mass production environments.

 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666