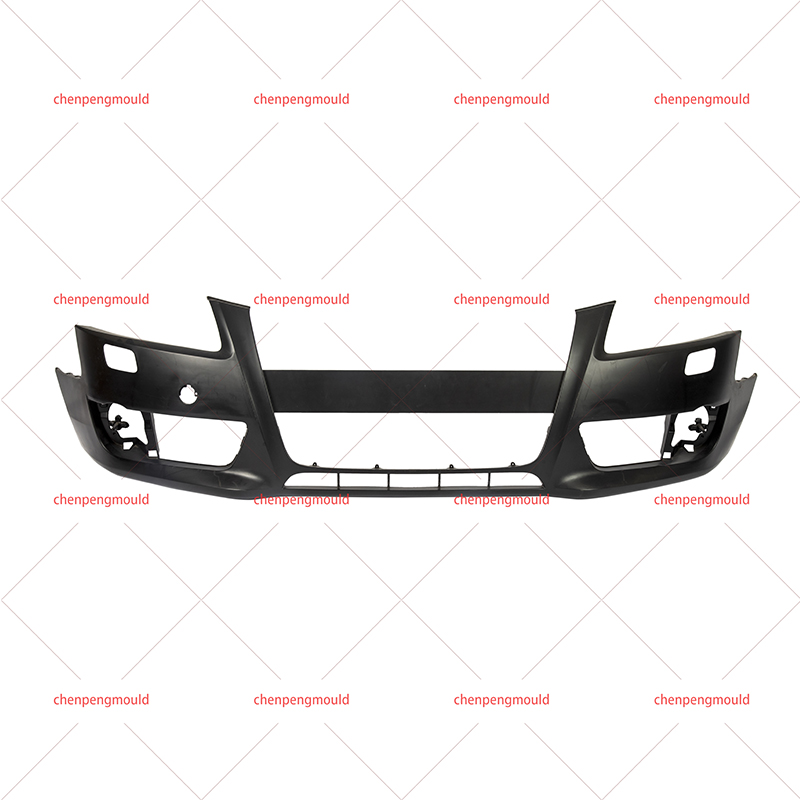
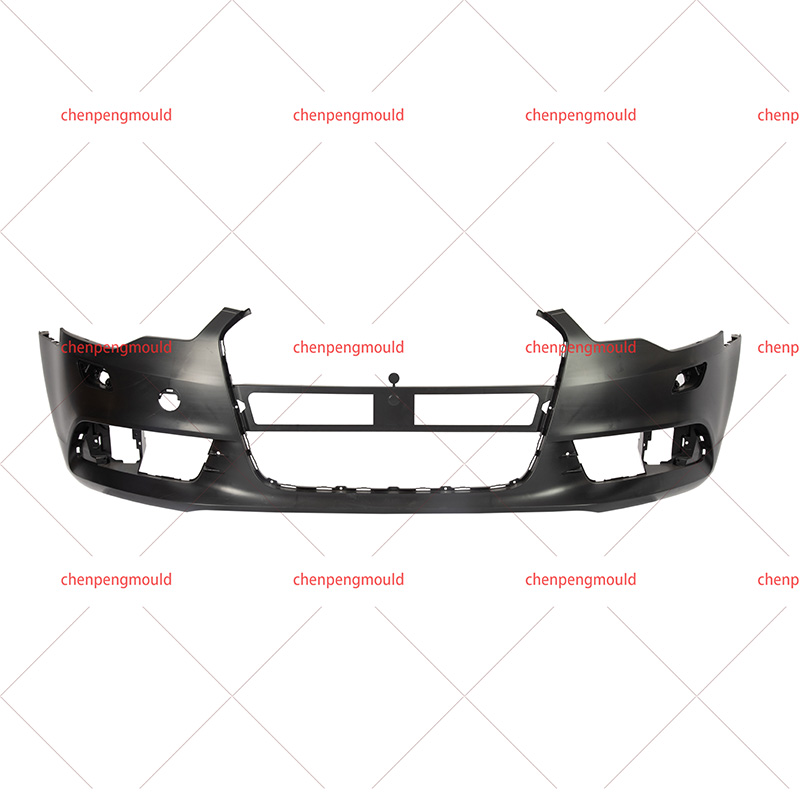
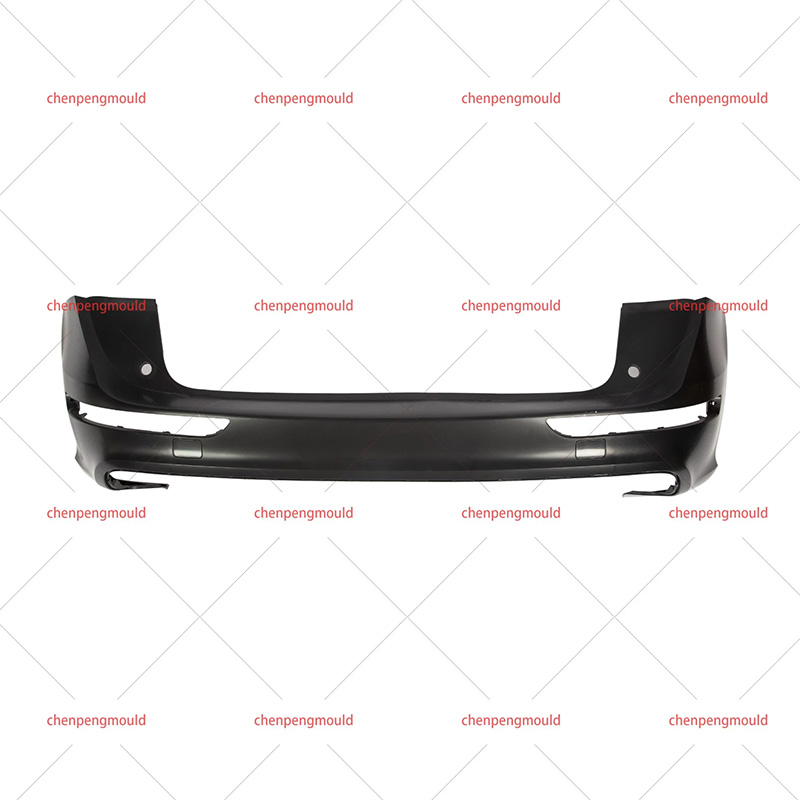
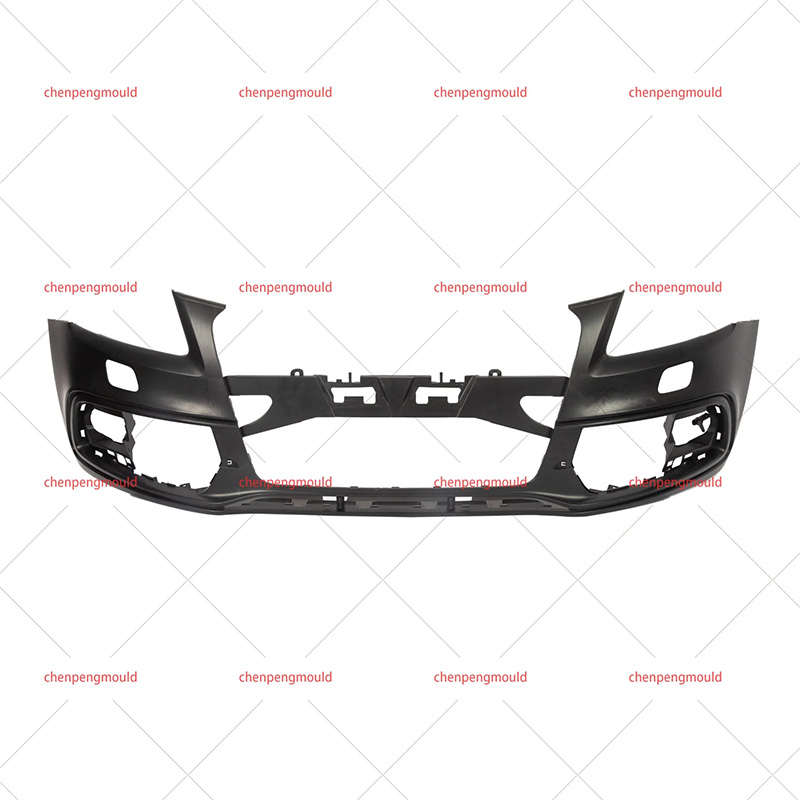
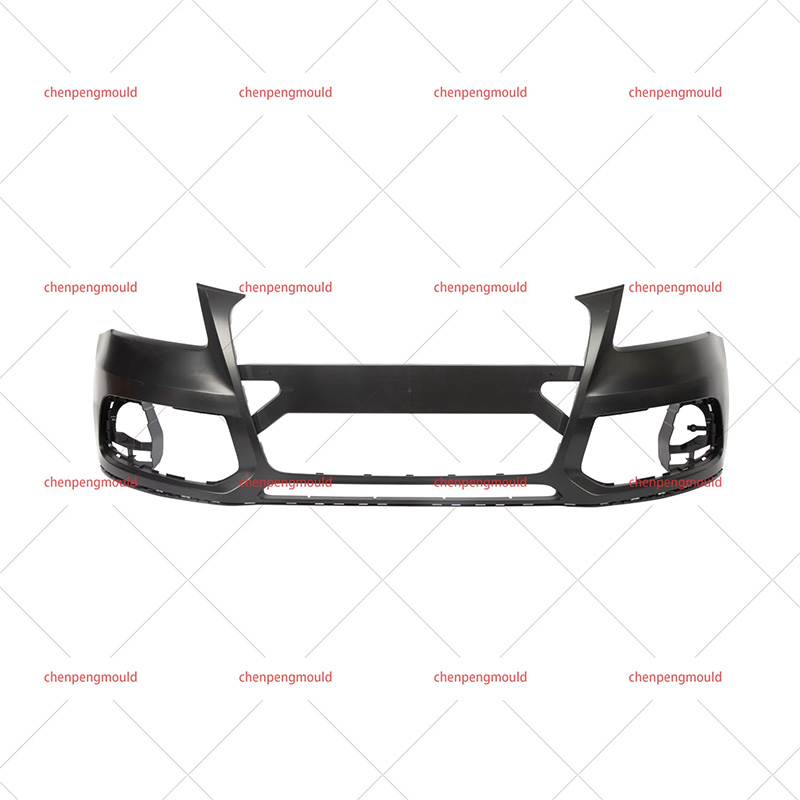
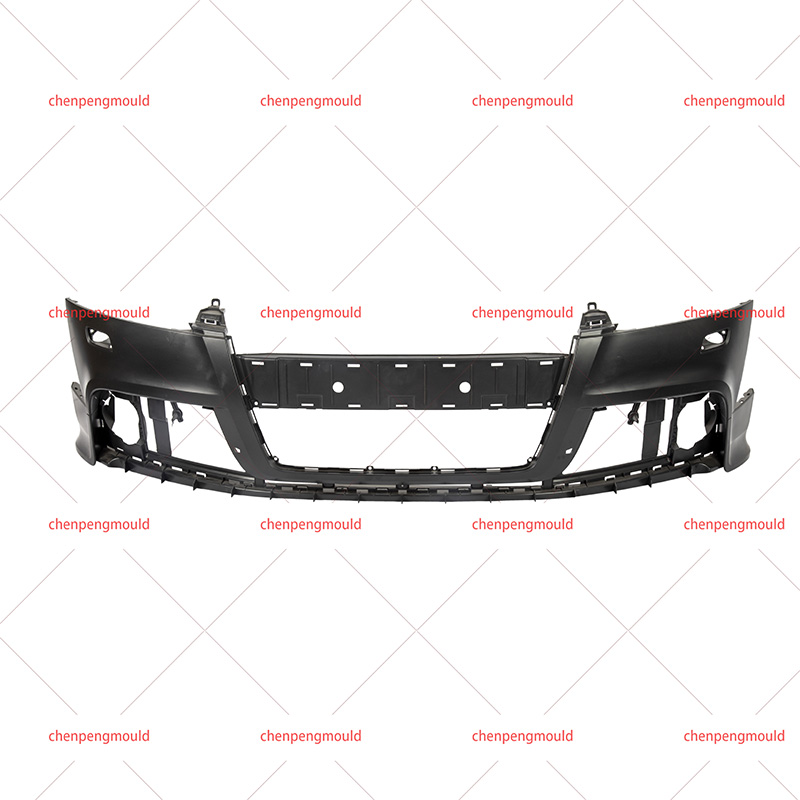
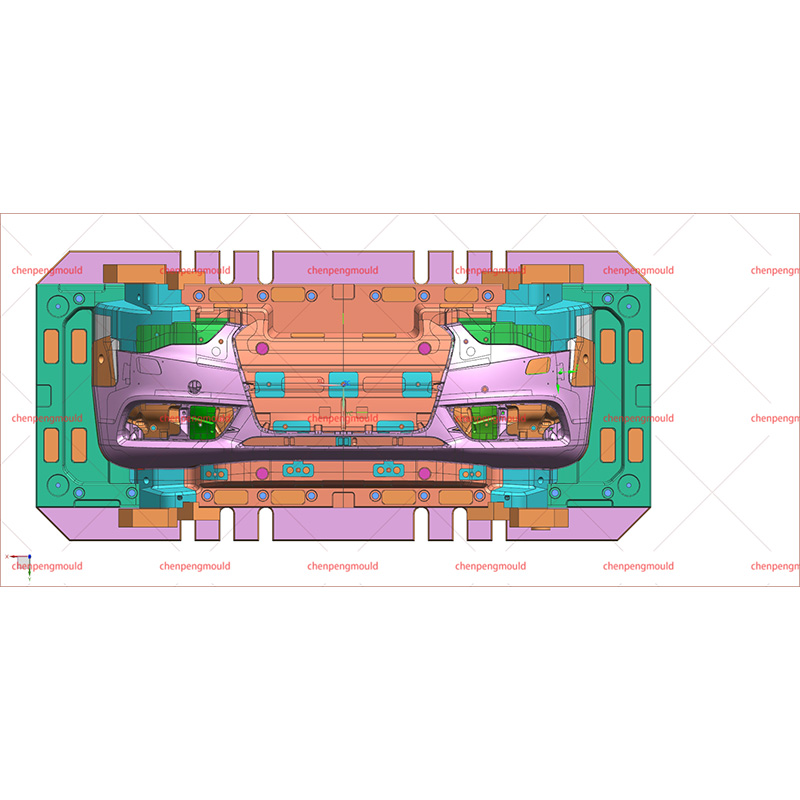
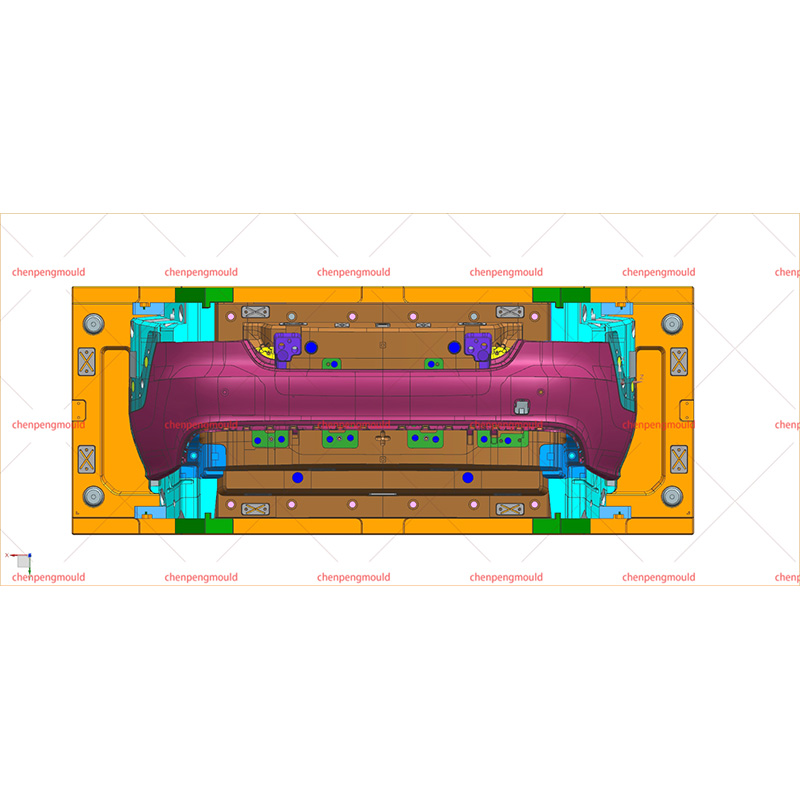
The middle grille mould plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of automotive grilles, which are an essential component of vehicle design. These grilles not only enhance the vehicle's aesthetics but also serve functional purposes, such as air circulation to the engine and cooling systems. Choosing the right middle grille mould is a key decision for manufacturers looking to produce high-quality, durable, and visually appealing grilles.
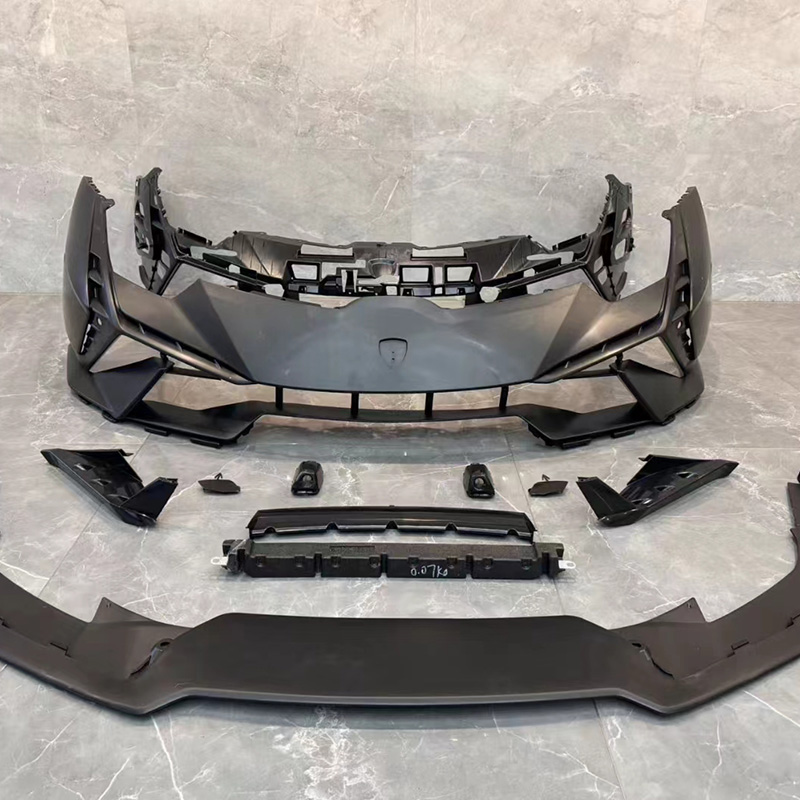

Middle grille moulds are typically designed to accommodate the vehicle's specific grille dimensions and airflow requirements, making precision in the design and construction of the mould essential for a successful final product.
The material used in the middle grille mould directly affects the durability, performance, and appearance of the final product. Common materials used for grilles include:
Plastic (ABS, Polypropylene, etc.): These materials offer flexibility, resistance to impact, and finishing qualities. They are popular in automotive grilles due to their ability to withstand various weather conditions.
Aluminum: In some cases, aluminum is used for its strength and ability to handle higher temperatures, although it may not be as commonly used as plastic in grille applications.
Stainless Steel: Used for its durability, resistance to corrosion, and premium appearance, stainless steel is sometimes chosen for higher-end vehicles.
When selecting a middle grille mould, ensure the material chosen aligns with the vehicle's functional requirements, aesthetic goals, and production capabilities.
The complexity of the grille design will determine the intricacy of the mould required. A more complex design, such as a grille with multiple integrated components (e.g., lights, logo holders, or intricate patterns), will demand a more sophisticated mould.
Key design considerations include:
Detailed Features: Grilles with fine patterns, logos, or vents require precise moulding to ensure high-quality detail.
Flowability: The mould must allow for proper flow of the material to avoid defects like warping or incomplete mould filling.
Mould Cavities: For mass production, multi-cavity moulds allow for multiple parts to be produced in one cycle, improving efficiency and reducing production costs.
Choosing a mould that can produce the desired level of detail while maintaining manufacturability is crucial.
A middle grille mould must be designed to withstand multiple production cycles without deteriorating. The longevity of the mould is influenced by:
Material of the Mould: Steel is commonly used for high-durability moulds, while softer materials may wear out more quickly.
Wear Resistance: Regular exposure to high temperatures and pressure can cause wear and tear, so ensuring the mould has proper coatings or heat treatment to resist corrosion and damage is important.
A durable mould ensures consistent product quality and reduces the need for frequent replacements or repairs, lowering long-term production costs.
The middle grille mould must be compatible with the specific injection moulding process used in the factory. The type of machine, injection pressure, and cooling systems must align with the mould's design for performance. Factors to consider include:
Injection Speed: High-speed injection may be necessary for large or complex parts.
Cooling Systems: A well-designed cooling system within the mould helps to prevent defects such as warping by ensuring even cooling during the solidification process.
Ejector Mechanisms: Properly designed ejector pins or mechanisms are critical to ensure that the finished part is removed cleanly from the mould without damaging the product.
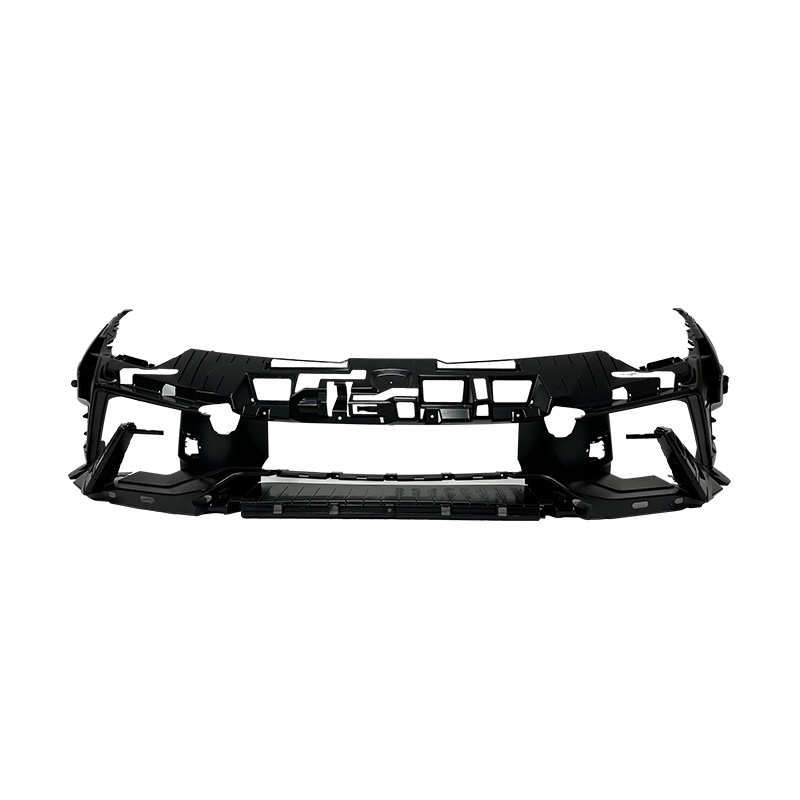




 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666