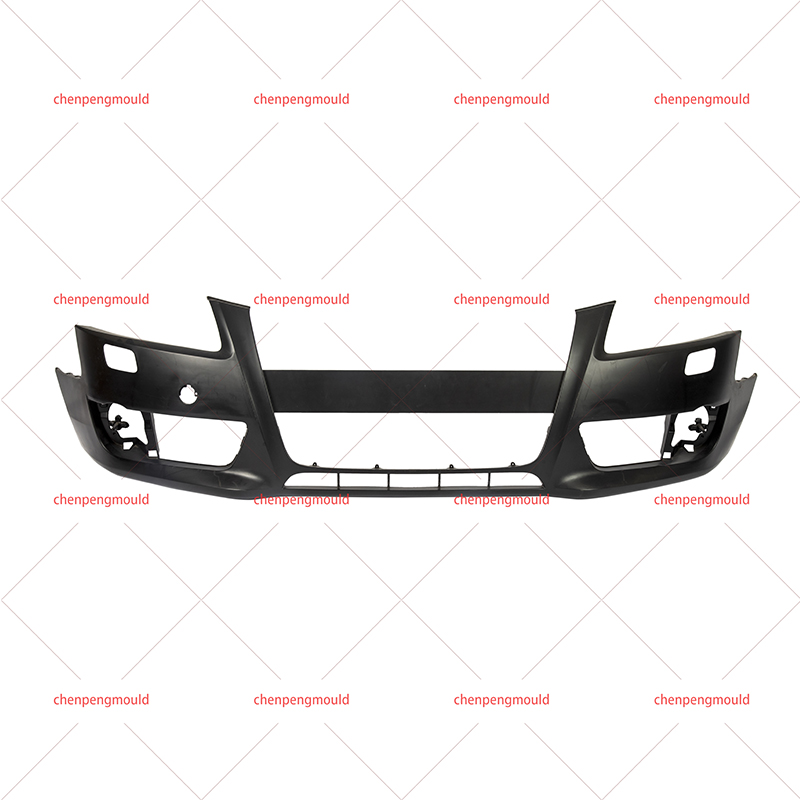
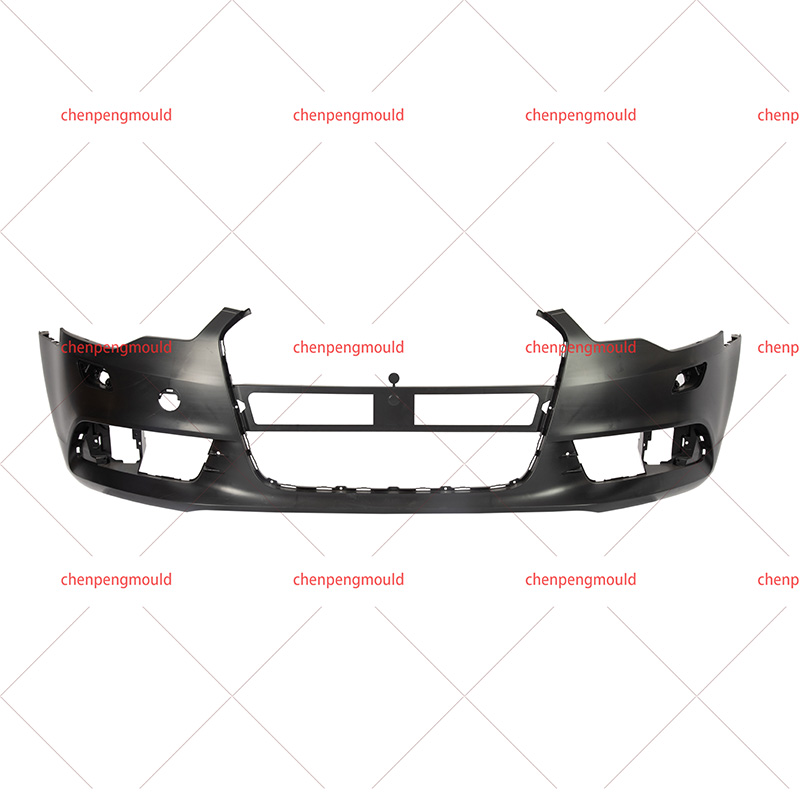
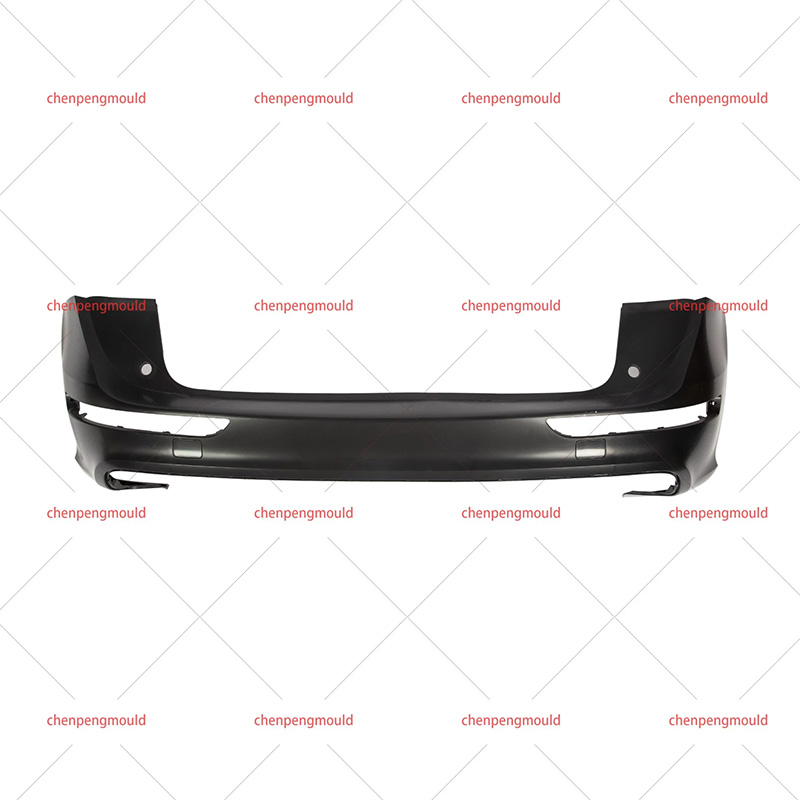
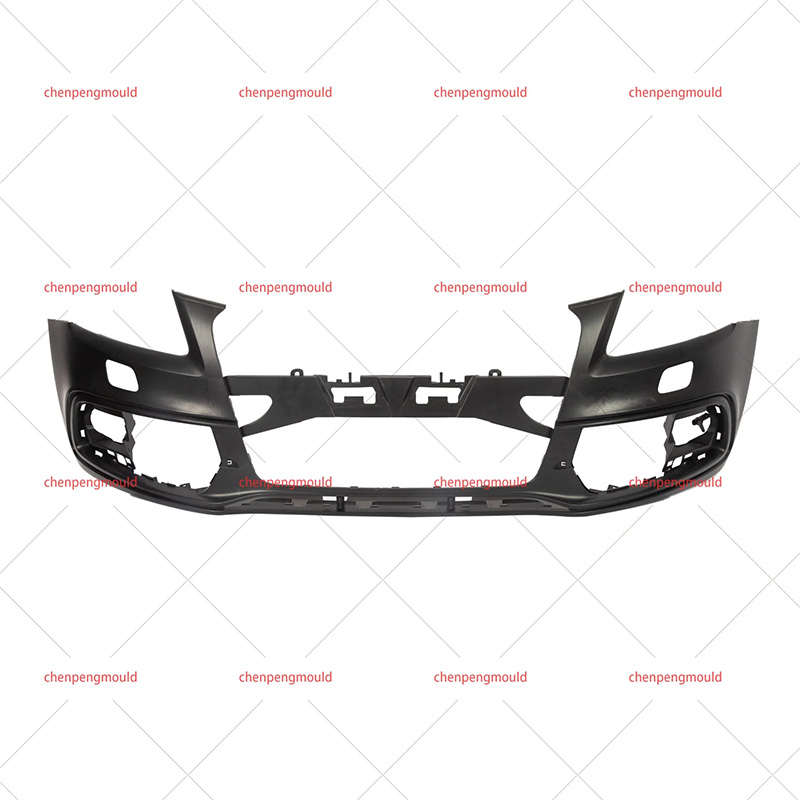
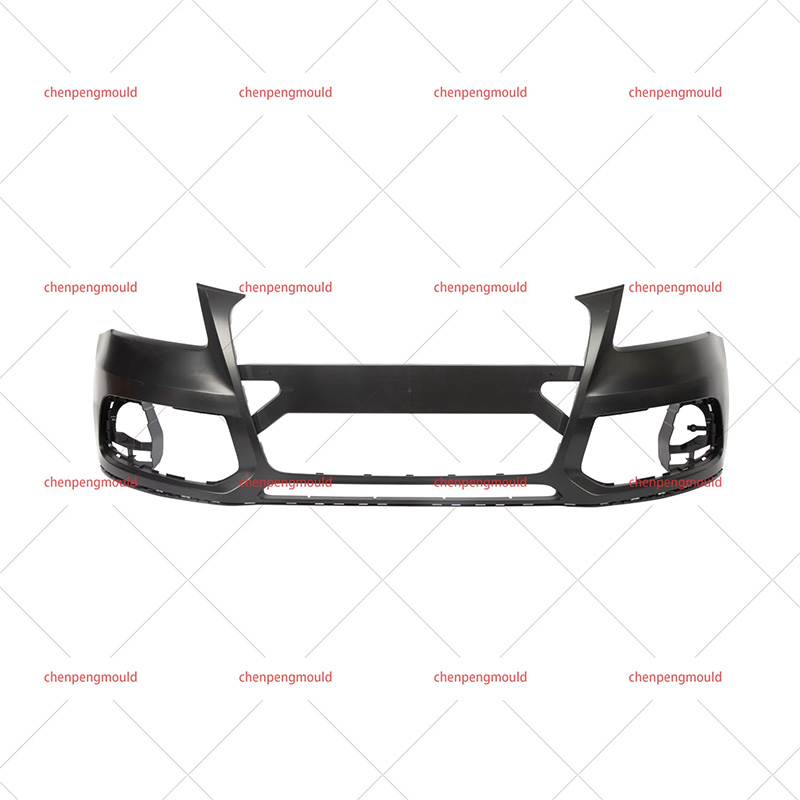
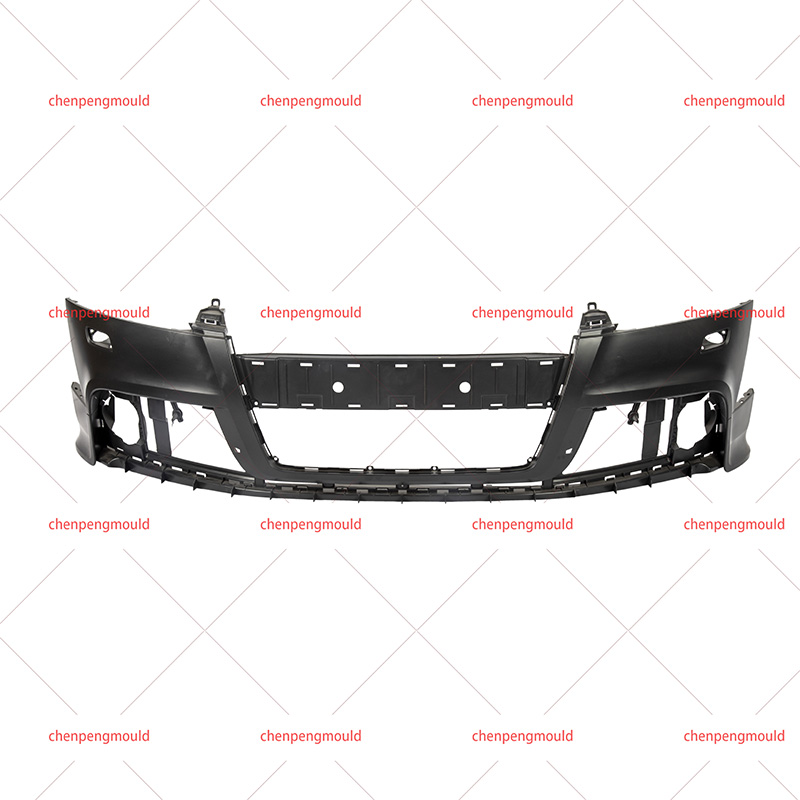
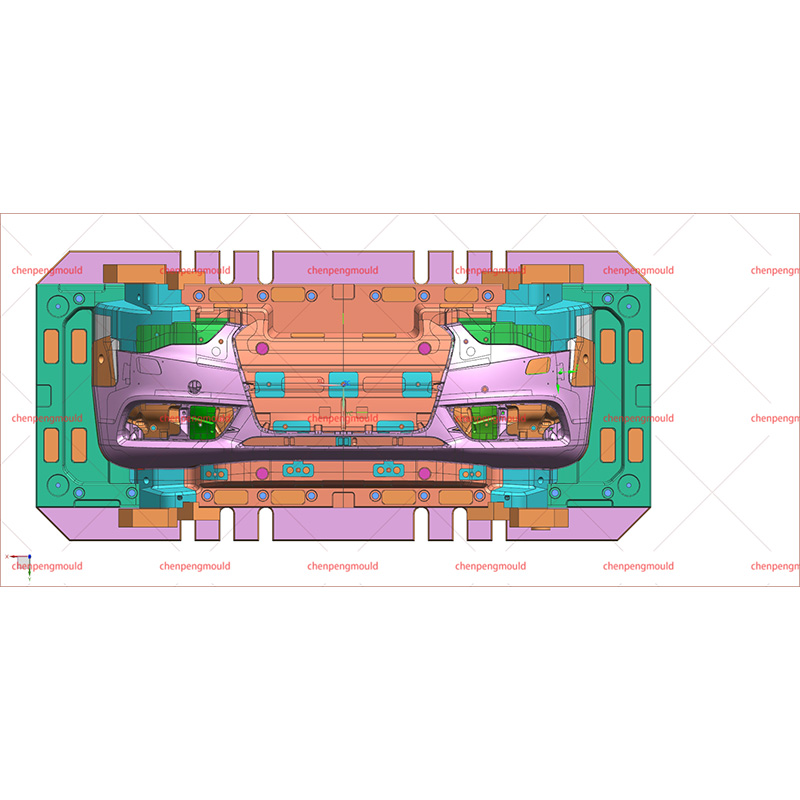
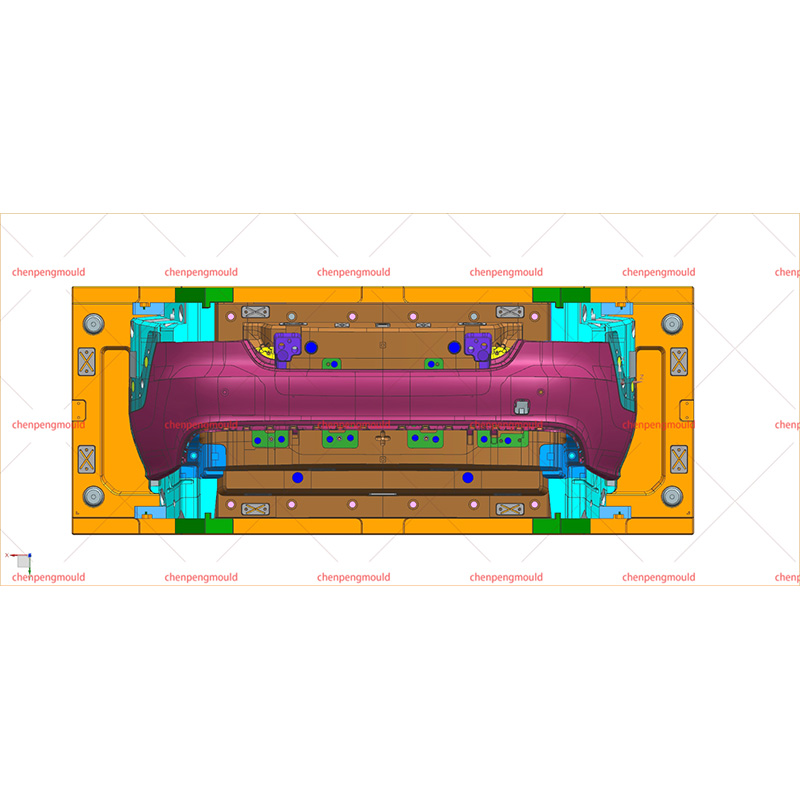
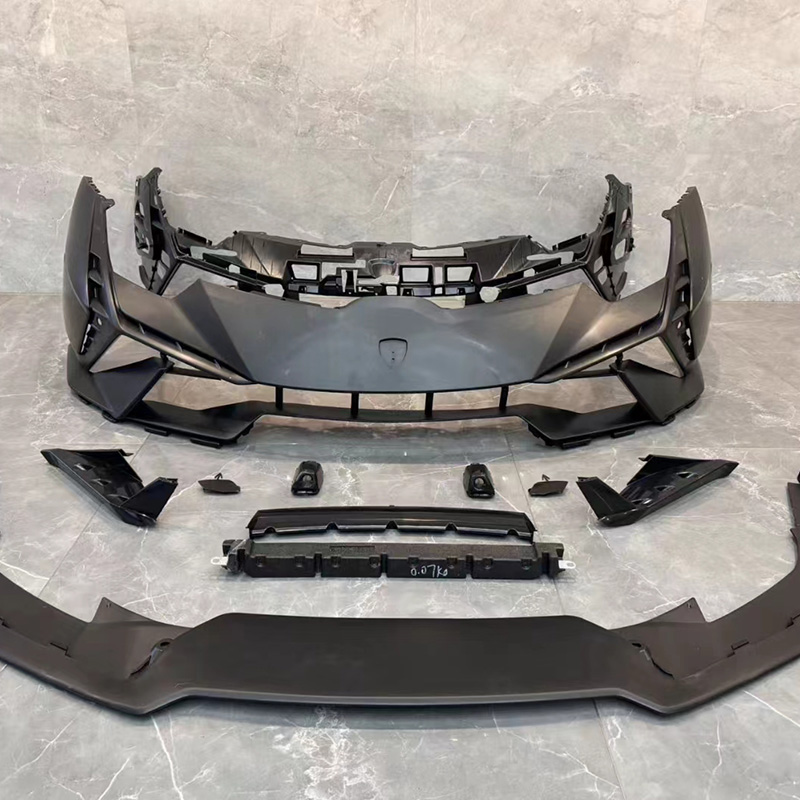
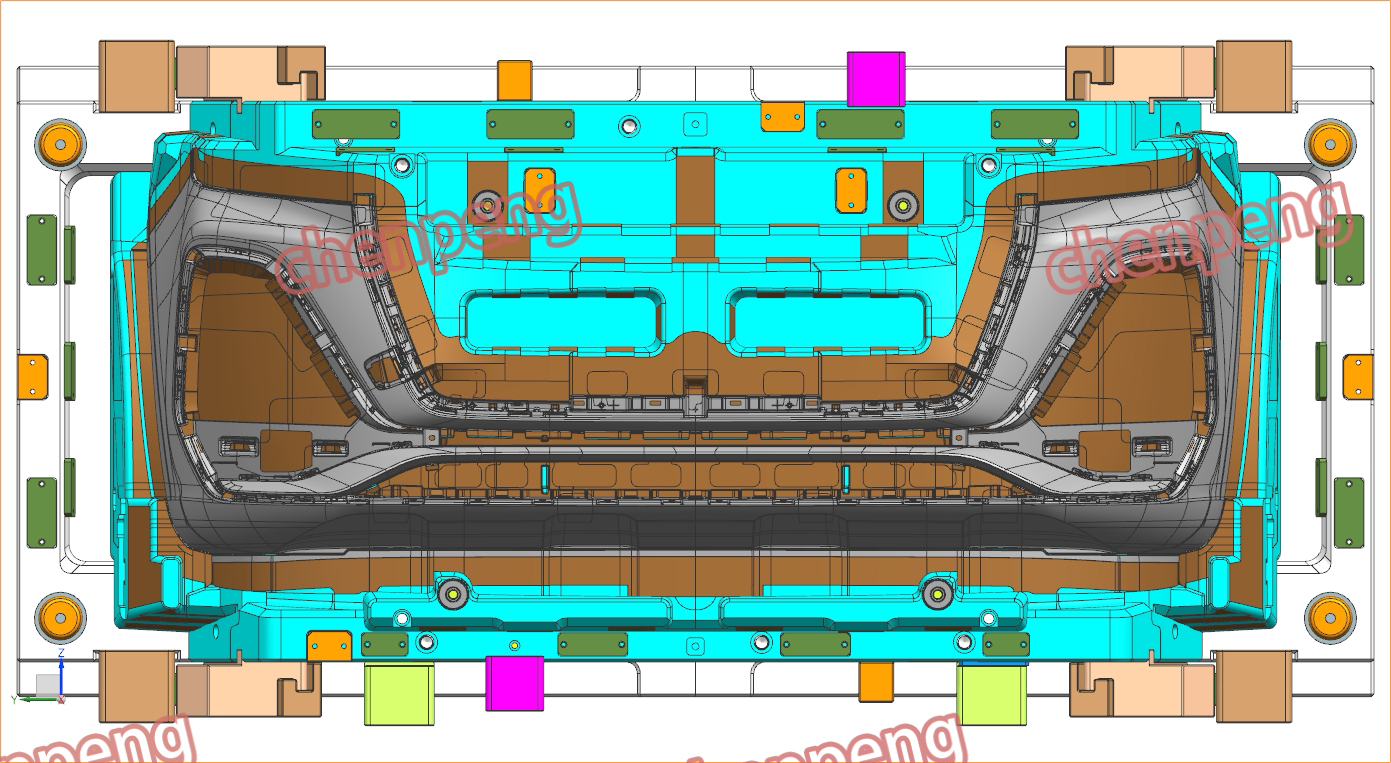
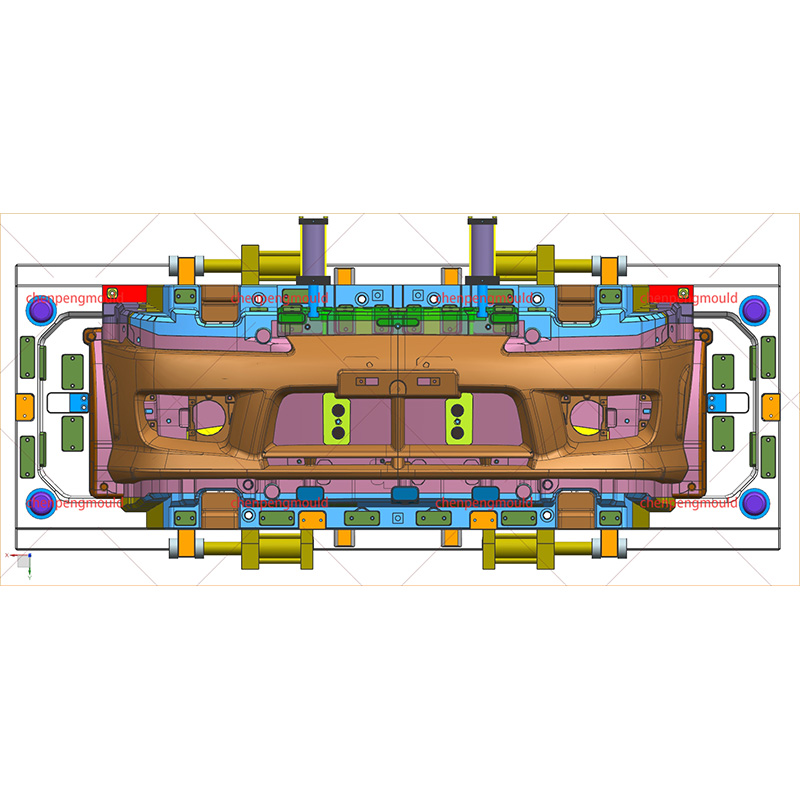
An auto parts mould is a specialized tool used in the process of manufacturing automotive components. Moulds serve as the templates for shaping raw materials, often metal or plastic, into finished car parts with precise dimensions and features. These parts can range from simple brackets to complex dashboards and bumpers. The choice of moulding process depends on the material, the complexity of the part, the production volume, and the specific requirements of the automotive part being manufactured.

The use of auto parts moulds in automotive production allows for high-speed manufacturing, high precision, and the ability to produce complex shapes, making them indispensable in modern vehicle manufacturing.
Types of Auto Parts Moulds
There are several types of auto parts moulds, each suited for different applications based on factors such as material, part complexity, and production volume. The common moulding techniques include:
Injection Moulding
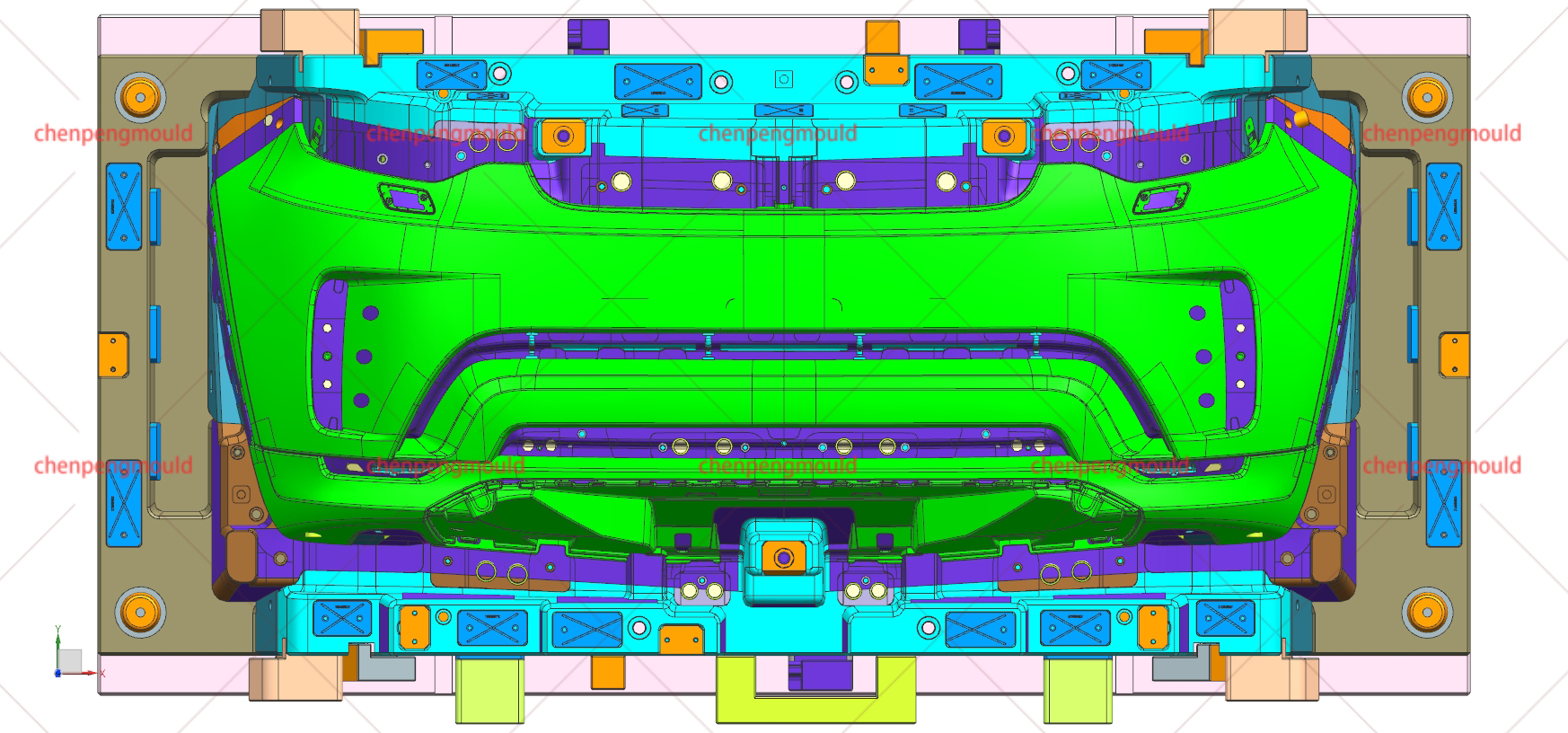
Injection moulding is one of the widely used methods in the production of automotive parts. It involves injecting molten material, typically plastic or metal, into a mould under high pressure. This process is ideal for producing high volumes of small to medium-sized parts with intricate shapes. Examples of components produced via injection moulding include interior parts like dashboards, door panels, and clips.
Injection moulding is favored for its precision, repeatability, and efficiency. However, it requires significant upfront costs for mould creation, making it more suitable for high-volume production runs.
Die-Casting Moulds
Die-casting is a process in which molten metal, usually aluminum, is forced into a steel mould at high pressure. This technique is primarily used for producing parts that require a high degree of strength, such as engine blocks, gearbox housings, and various structural components. Die-casting is known for its ability to produce complex shapes with dimensional accuracy.
While the initial cost of die-casting moulds is high, the process offers long-term cost efficiency in high-volume production due to its ability to produce parts quickly and with minimal waste.
Compression Moulding
Compression moulding is typically used for producing rubber or composite parts, such as seals, gaskets, and other flexible components used in automotive manufacturing. In this process, the material is placed into an open mould, and pressure is applied to form the part. Heat is also used to cure the material, ensuring that it holds its shape.
Compression moulding is often chosen for parts that require flexibility, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. The technique is also highly effective for producing parts in larger sizes and is often used in the production of automotive seals and weatherstripping.
Blow Moulding
Blow moulding is a process commonly used for producing hollow parts, such as fuel tanks, reservoirs, and air ducts. In this process, a tube of molten plastic is inflated inside a mould, shaping the material into the desired form. Blow moulding offers significant flexibility in terms of the shapes it can create and is particularly useful for parts that require an internal cavity.
While the setup costs can be high for custom moulds, blow moulding is highly cost-effective in producing large quantities of hollow automotive parts.
Rotational moulding involves the heating of a hollow mould while it is rotated along two perpendicular axes. This process is used to produce large, hollow parts, such as bumpers, fuel tanks, and storage containers. The main advantage of rotational moulding is its ability to produce large and complex parts without the need for high pressure.
Rotational moulding is cost-effective when producing low to medium volumes of parts, especially when the parts are relatively simple in design.

 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666