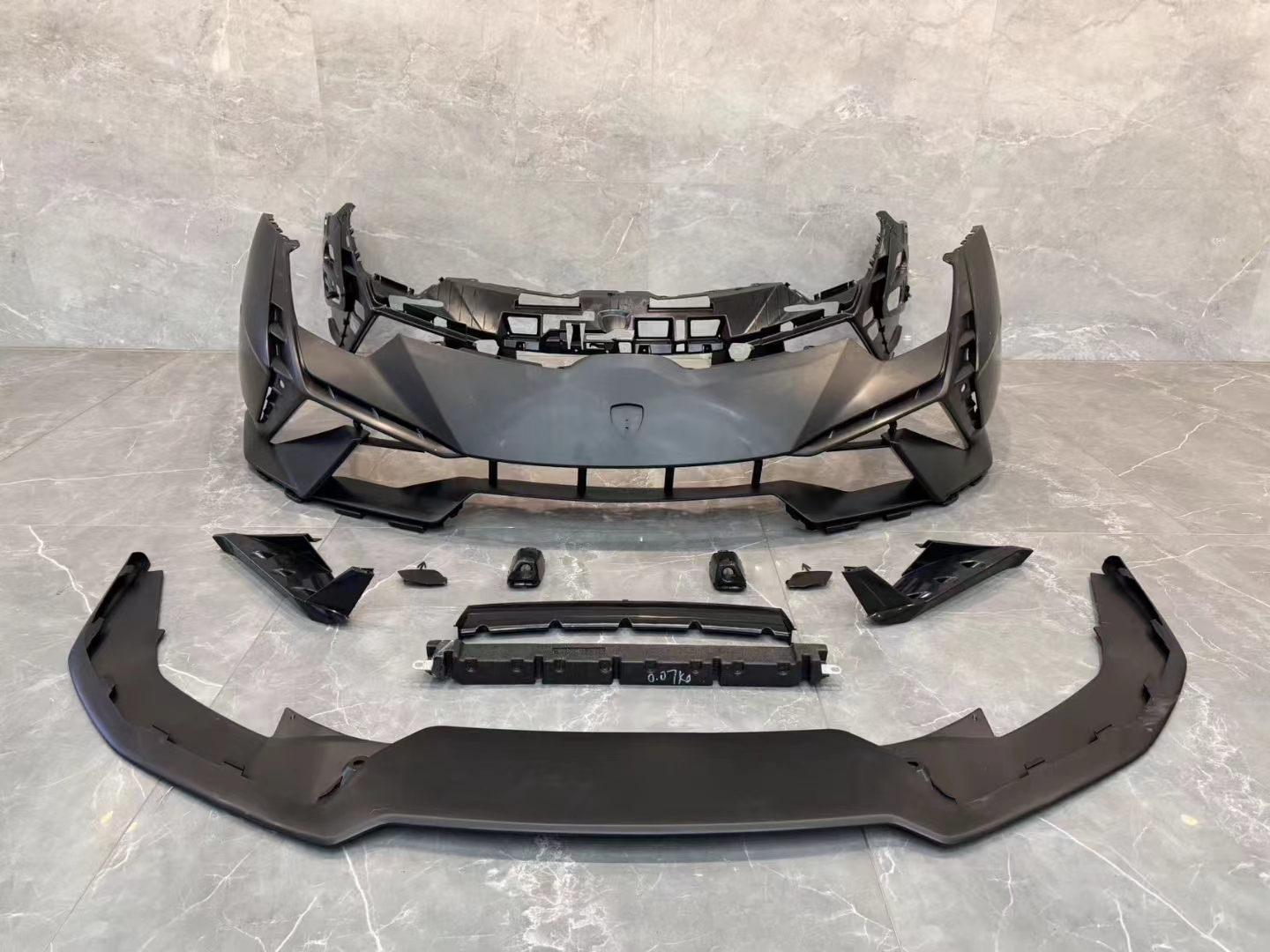
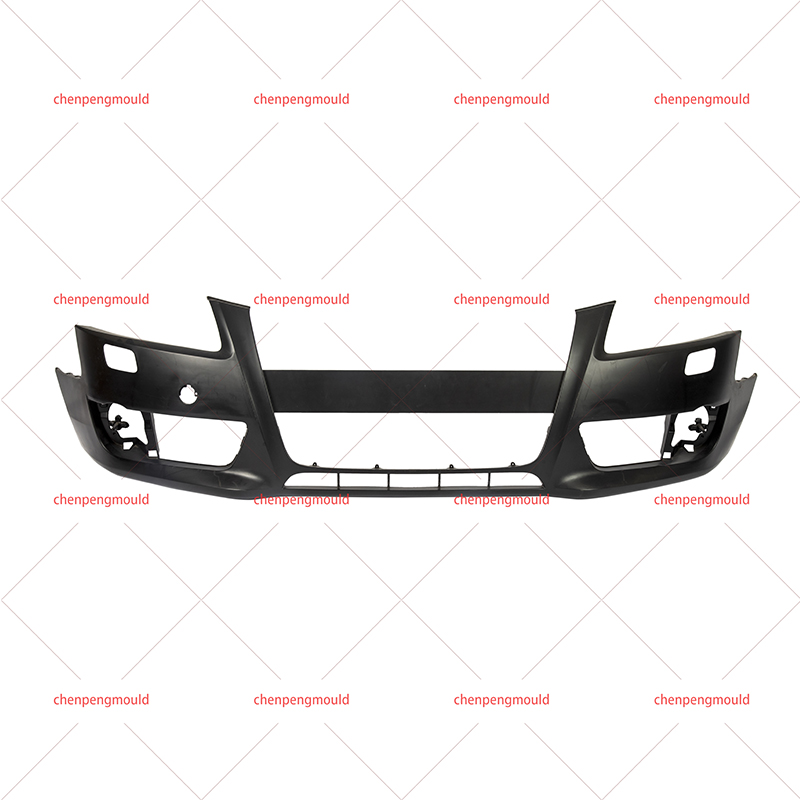
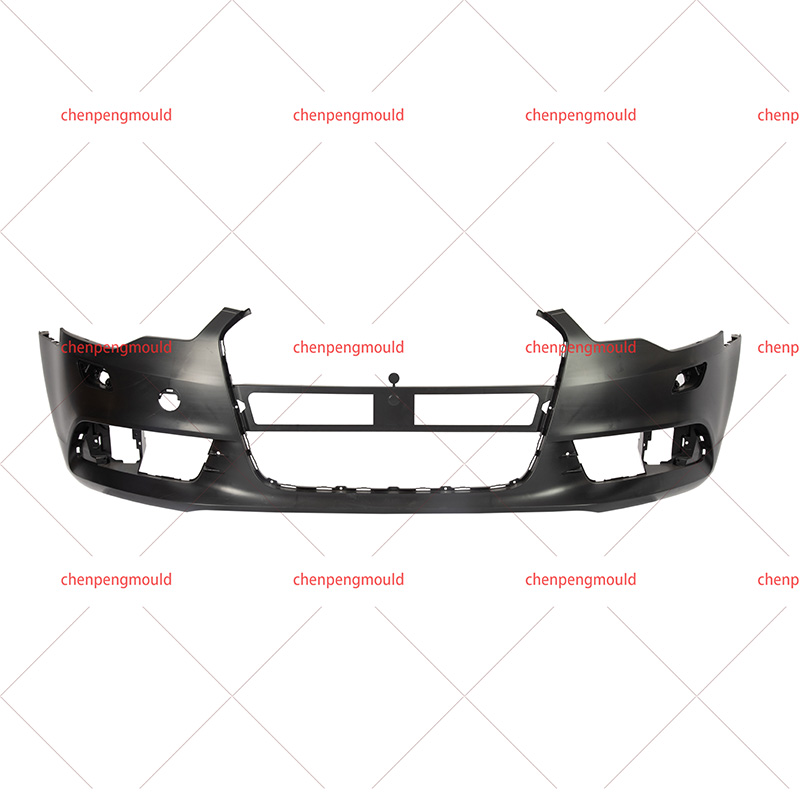
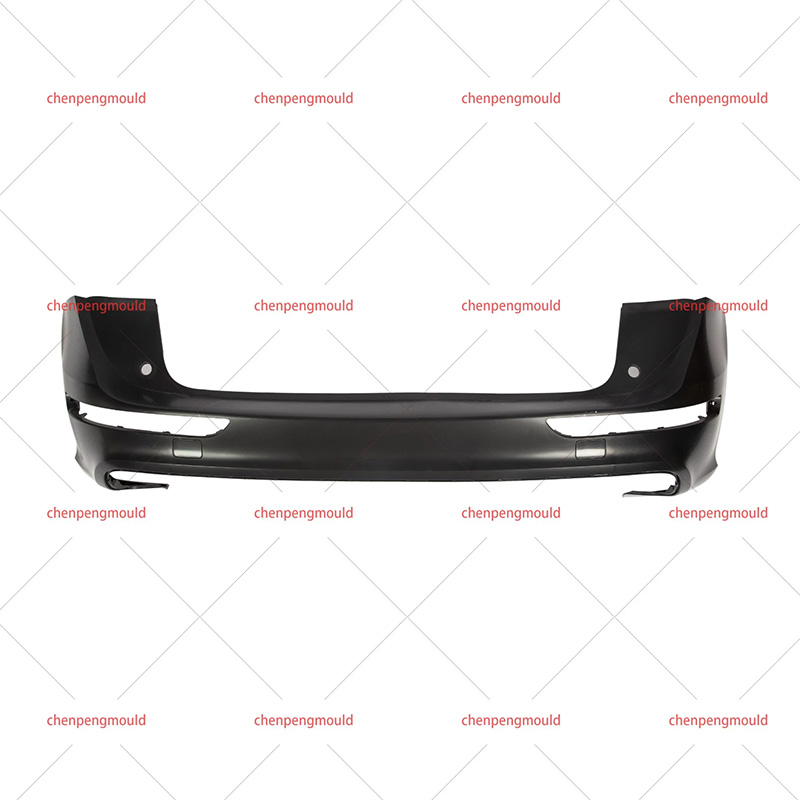
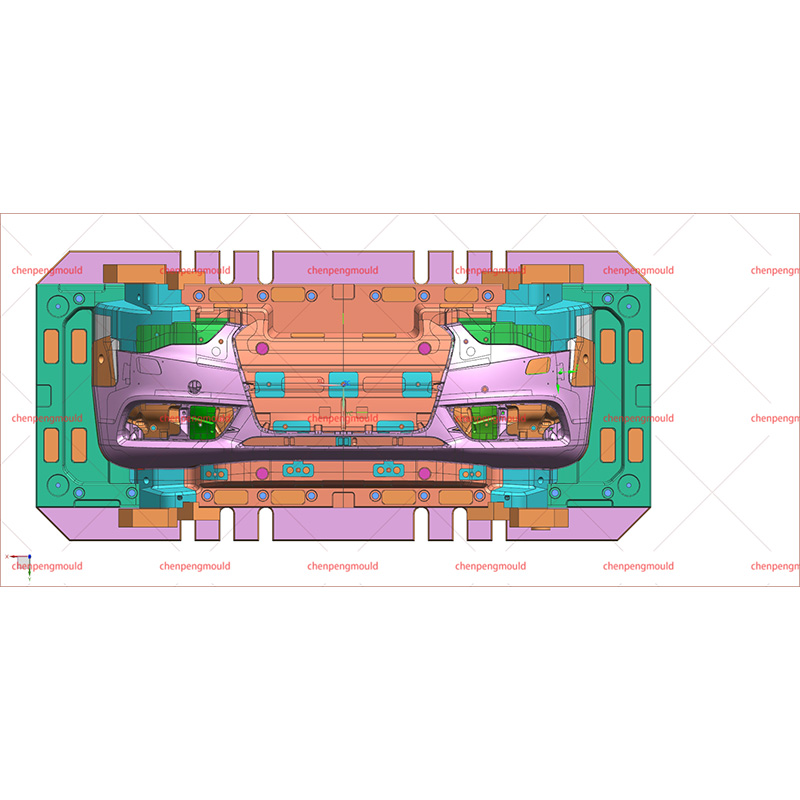
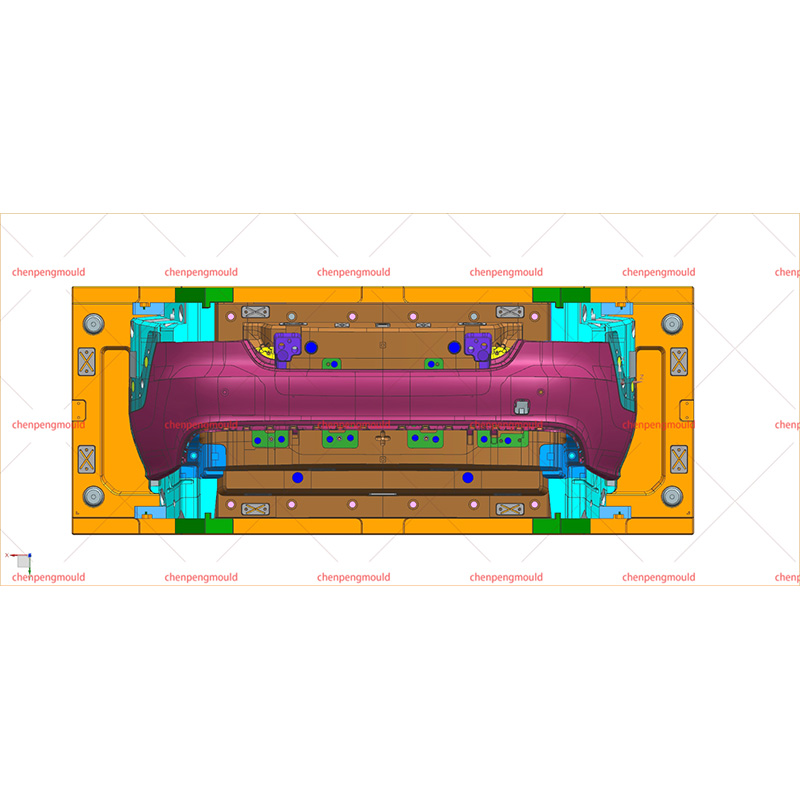
Materials Used in Bumper Molding
Material selection is one of the critical factors in bumper molding choice. The common materials used include:
Thermoplastic Olefin (TPO): Known for its impact resistance and flexibility, TPO is widely used in bumper molding due to its durability and ability to withstand temperature variations without cracking or warping.
Polypropylene (PP): This material offers good chemical resistance and is lightweight. When reinforced with additives like talc or glass fibers, PP can deliver enhanced stiffness and strength.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE): These materials provide rubber-like flexibility, which helps in absorbing minor impacts and improving the bumper's protective function.
Polyurethane (PU): Often used in bumpers requiring a softer touch or higher elasticity, PU molding provides resistance to abrasion and weathering.
Each material has specific advantages and trade-offs in terms of cost, weight, finish quality, and ease of processing.
Manufacturing Methods
The manufacturing process influences the choice of bumper molding material and design complexity:
Injection Molding: This is the common method, especially for thermoplastics. Injection molding allows for high precision and repeatability, making it suitable for mass production. It enables the creation of complex shapes and integrated design features like mounting points and textures.
Extrusion: For simpler, linear molding profiles, extrusion is cost-effective. However, it limits the complexity of shapes achievable and may require secondary processes like cutting or shaping.
Compression Molding: Used primarily for thermoset materials or composites, compression molding provides strong, durable parts but may have longer cycle times.
Manufacturers must consider the production volume, complexity, and required finish quality when choosing the molding method.
Durability and Performance
Since bumpers protect vehicles from minor collisions and abrasions, the durability of the molding material is vital. Important performance factors include:
Impact Resistance: The molding should absorb minor impacts without cracking or permanent deformation.
Weather Resistance: Exposure to sunlight, rain, and temperature changes can degrade materials. UV stabilizers and corrosion-resistant additives help extend the life of bumper moldings.
Chemical Resistance: The molding should resist damage from automotive fluids, road salts, and cleaning agents.
Flexibility: Some flexibility helps moldings conform to bumper shapes and absorb shocks.
Materials and designs that optimize these factors enhance the protective function and reduce maintenance costs.
Design and Aesthetic Considerations
Bumper moldings contribute significantly to a vehicle's exterior styling. Factors affecting the design choice include:
Surface Finish: Smooth, textured, or matte finishes can be achieved based on material and molding process. These finishes affect the visual appeal and scratch resistance.
Color Matching: Moldings can be color-matched with vehicle paint to blend seamlessly or contrast for styling effects. Some materials accept paint better than others, influencing the choice.
Integration with Vehicle Lines: The molding design should complement the overall shape of the bumper and vehicle body, maintaining aerodynamics and visual harmony.
Automakers often work closely with designers to ensure the molding supports brand identity and consumer preferences.
Cost and Production Efficiency
Cost remains a practical consideration. While premium materials and complex molding processes deliver better aesthetics and durability, they also raise production costs. Balancing initial manufacturing expenses with long-term performance and maintenance savings is important.
Bulk production capabilities, availability of raw materials, and ease of assembly influence cost-efficiency. Suppliers capable of delivering consistent quality with short times often become preferred partners.

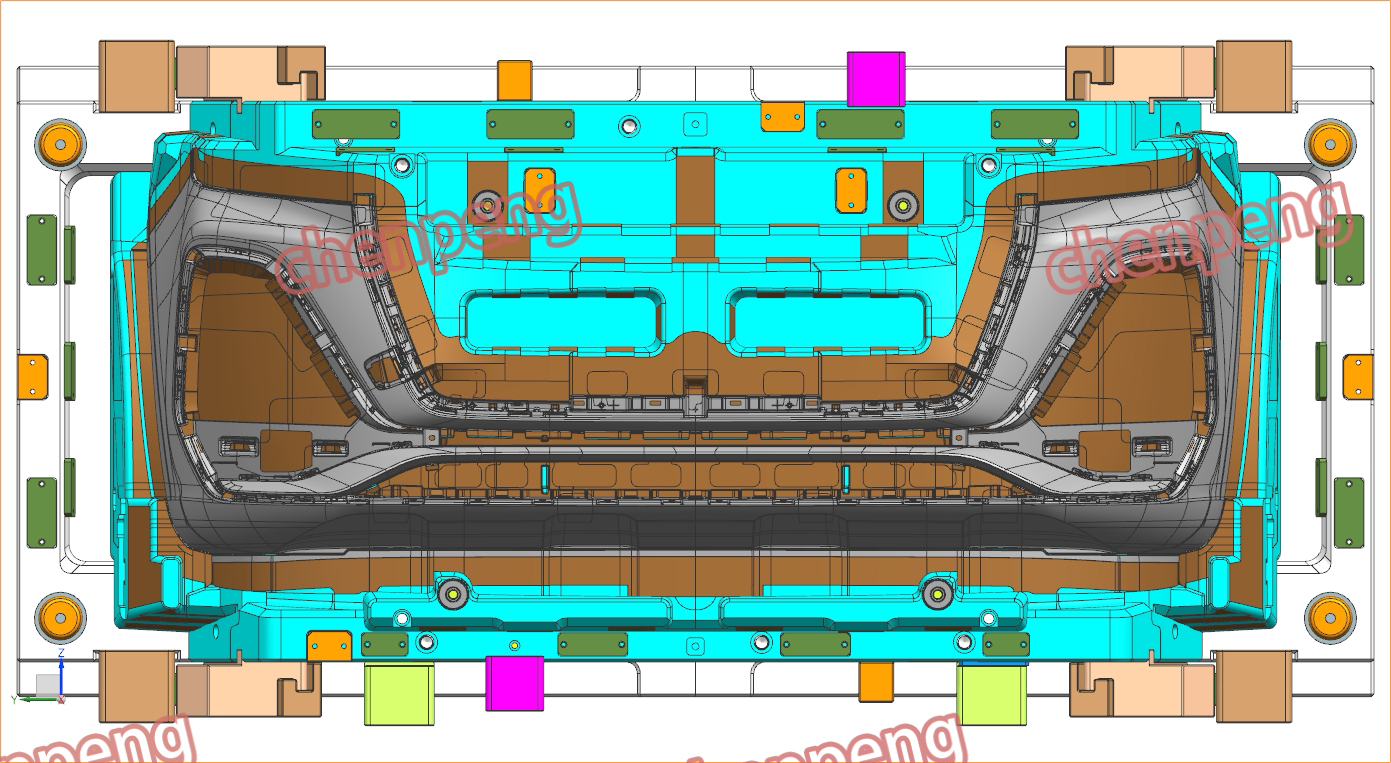
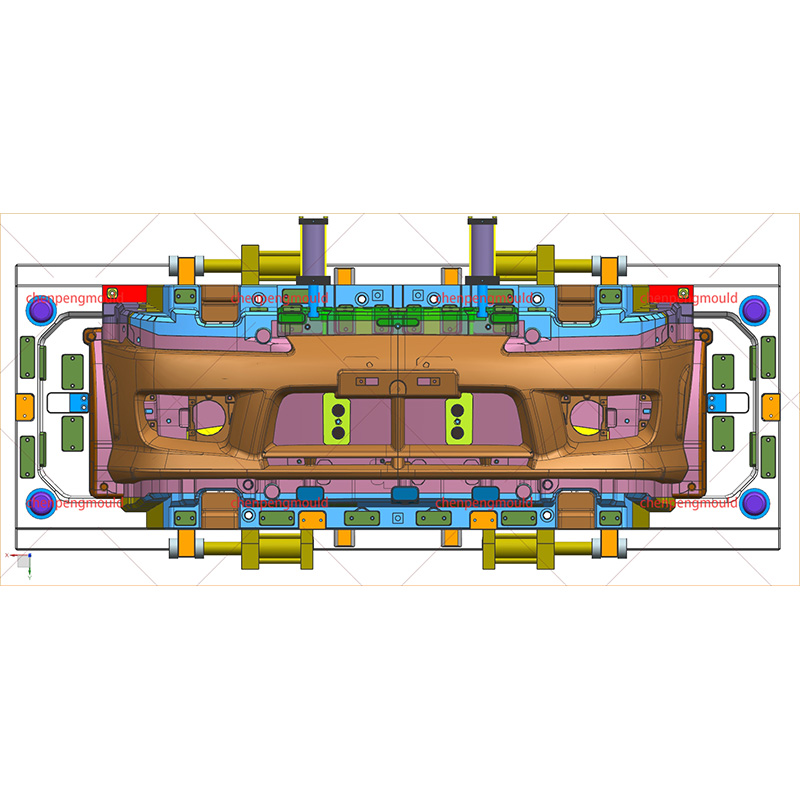
 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666